RNA-Seq analysis for non-model organisms
- Authors
Olabiyi Obayomi, Menachem Sklarz, Liron Levin, Vered Chalifa-Caspi
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics Core Facility
- Organization
Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva.
Introduction
Human and model organisms, such as mouse and Arabidopsis, typically have high quality genome sequences which can serve as reference for RNA-Seq analysis, and a rich assortment of tools are available for their downstream functional and pathway analyses. In contrast, non-model organisms usually have low quality (draft) genome references or none at all, and a limited number of tools for their functional and pathway analyses. For a microbial organism with a small genome size, genome sequencing may solve the problem of a lack of reference genome for RNA-Seq analysis. However, as the genome of interest becomes larger and contains more repeat regions, achieving a genome reference becomes very expensive and difficult. Due to this problem, it is often preferred to use for the analysis, a reference transcriptome assembled from the sequenced RNA-Seq reads of the organism of interest 1 . Consequently, this pipeline was developed for the analysis of RNA-Seq reads of non-model organisms and as a companion to the article 1 written by Dr. Vered Chalifa-Caspi. This pipeline performs an automated analysis of RNA-Seq reads, from quality assessment and preprocessing of the reads to transcriptome assembly and annotation, read alignment and quantification, statistical testing for differential expression, clustering, and function enrichment analyses. The pipeline is divided into sections called tags in the non-model_RNA_Seq.yaml parameter file supplied with this pipeline. Each section and its steps are summarized graphically and in a table then described breifly below. On the schema below, different colors represent different sections or tags in the pipeline.
Pipeline Schema
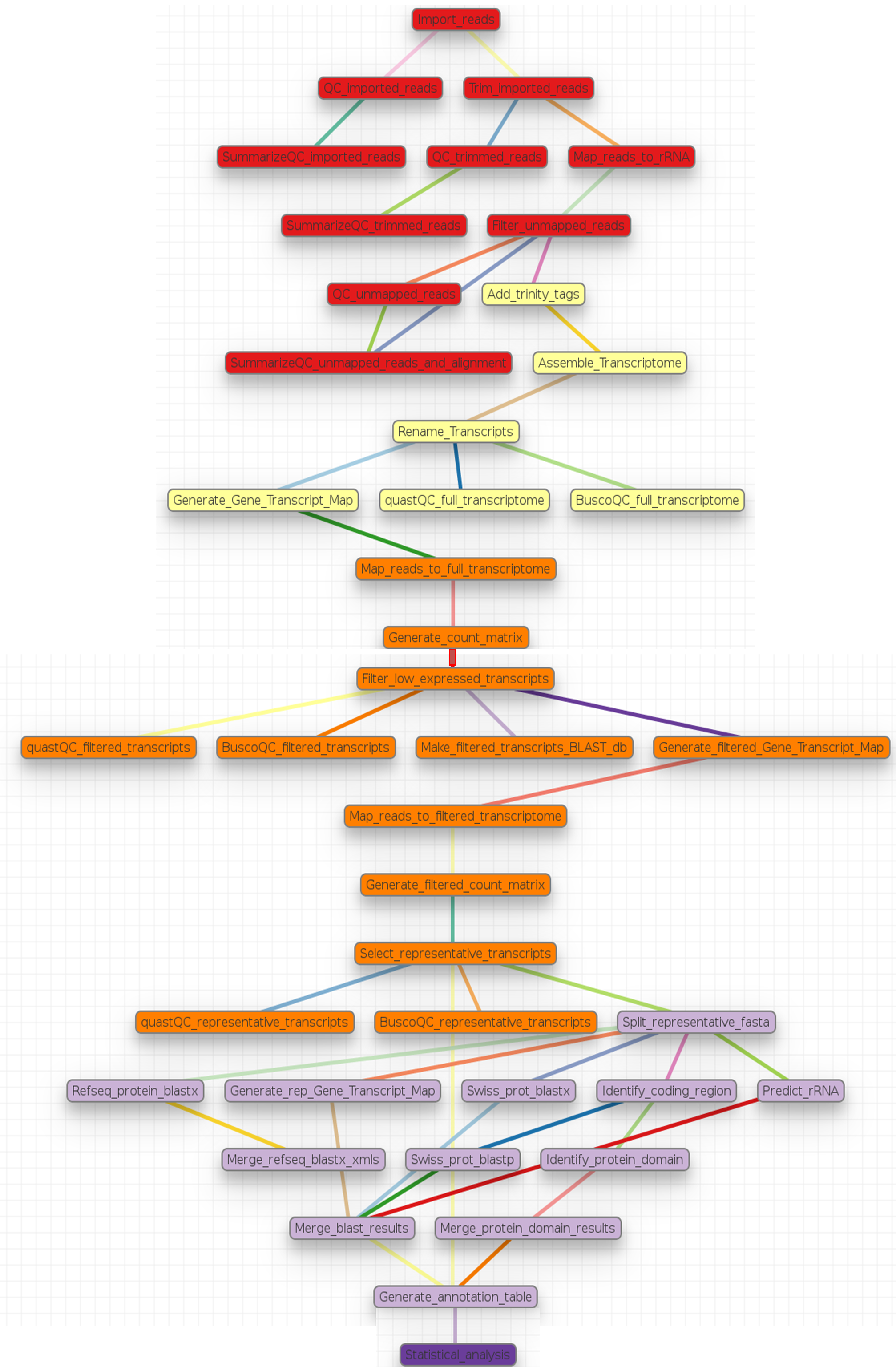
A summary of steps in the pipeline
Step |
Step name in book 1 |
Module |
Program |
|---|---|---|---|
Import_reads |
import reads |
Import |
gzip |
QC_imported_reads |
QA: FastQC |
fastqc_html |
fastqc |
SummarizeQC_imported_reads |
Summarize QA: MultiQC |
Multiqc |
MultiQC |
Trim_imported_reads |
Trim imported reads |
Trim_Galore |
trim_galore |
QC_trimmed_reads |
QA: FastQC |
fastqc_html |
fastqc |
SummarizeQC_trimmed_reads |
Summarize QA: MultiQC |
Multiqc |
MultiQC |
Map_reads_to_rRNA |
Align reads to rRNA |
bwa_mapper |
bwa |
Filter_unmapped_reads |
Process alignments & retain unaligned reads |
samtools |
samtools |
QC_unmapped_reads |
QA: FastQC |
fastqc_html |
fastqc |
SummarizeQC_unmapped_reads_and_alignment |
Summarize QA: MiltiQC |
Multiqc |
MultiQC |
Add_trinity_tags |
Format FASTQ files for Trinity |
add_trinity_tags |
awk |
Assemble_Transcriptome |
Assemble transcriptome |
trinity |
Trinity |
Rename_Transcripts |
Edit transcript names |
Generic |
seqkit |
quastQC_full_transcriptome |
QA: QUAST |
quast |
quast |
BuscoQC_full_transcriptome |
QA: BUSCO |
BUSCO |
BUSCO |
Generate_Gene_Transcript_Map |
Generate gene to transcript map |
trinity_mapping |
Trinity |
Map_reads_to_full_transcriptome |
Align reads and estimate abundance |
trinity_mapping |
Trinity |
Generate_count_matrix |
Generate abundance matrix |
trinity_statistics |
Trinity |
Filter_low_expressed_transcripts |
Filter low expressed transcripts |
Generic |
filter_trinity_by_counts.R |
quastQC_filtered_transcripts |
QA: QUAST |
quast |
quast |
BuscoQC_filtered_transcripts |
QA: BUSCO |
BUSCO |
BUSCO |
Make_filtered_transcripts_BLAST_db |
Make BLAST database |
makeblastdb |
makeblastdb |
Generate_filtered_Gene_Transcript_Map |
Generate gene to transcript map |
trinity_mapping |
Trinity |
Map_reads_to_filtered_transcriptome |
Align reads and estimate abundance |
trinity_mapping |
Trinity |
Generate_filtered_count_matrix |
Generate abundance matrix |
trinity_statistics |
Trinity |
Select_representative_transcripts |
Select representative transcript per gene |
Generic |
Trinity |
quastQC_representative_transcripts |
QA: QUAST |
quast |
quast |
BuscoQC_representative_transcripts |
QA: BUSCO |
BUSCO |
BUSCO |
Split_representative_fasta |
Split transcriptome fasta to n parts |
fasta_splitter |
fasta-splitter.pl |
Refseq_protein_blastx |
blastx vs. RefSeq protein |
blast |
blastx |
Merge_refseq_blastx_xmls |
Merge blastx XML results |
Generic |
BlastXMLmerge.py |
Generate_rep_Gene_Transcript_Map |
Generate gene to transcript map |
trinity_mapping |
Trinity |
Swiss_prot_blastx |
blastx vs. Swiss-Prot |
blast |
blastx |
Identify_coding_region |
Identify coding regions |
TransDecoder |
TransDecoder |
Swiss_prot_blastp |
blastp vs. Swiss-Prot |
blast |
blastp |
Identify_protein_domain |
Identify conserved protein domains |
hmmscan |
hmmscan |
Predict_rRNA |
Predict rRNA |
RnammerTranscriptome |
rnammer |
Merge_protein_domain_results |
Merge conserved domain results |
merge_tables |
awk |
Merge_blast_results |
Merge results |
merge_tables |
awk |
Generate_annotation_table |
Generate annotation table |
Trinotate |
Trinotate |
Statistical_analysis |
Statistical analysis |
DeSeq2 |
DESeq2 |
Section name - Description
00.Quality_check - Import and Quality check reads
Import_reads: Import forward and reverse reads based on information provided in the sample_data.nsfs file using
Importmodule.QC_imported_reads and SummarizeQC_imported_reads: Quality check the imported reads to guarantee their reliability with fastqc and summarize the results with multiqc using
fastqc_htmlandMultiqcmodules, respectively.Trim_imported_reads: Trim adaptors and low quality reads with trim galore using
Trim_Galoremodule. By default retains only reads that are at least 50 bp long and with an average Phred quality score of 20.QC_trimmed_reads and SummarizeQC_trimmed_reads: Quality check the trimmed reads with FastQC and summarize with MultiQC using
fastqc_htmlandMultiqcmodules, respectively.Map_reads_to_rRNA: Map the trimmed reads to the supplied rRNA database with bwa mem using the
bwa_mappermodule.Filter_unmapped_reads: Get the proportion of mapped reads using samtools flagstat command. Extract fastq files of unmapped read pairs from the alignment bam files using the samtools fastq command with the
samtoolsmodule.QC_unmapped_reads, SummarizeQC_unmapped_reads_and_alignment: Assess the quality of the unmapped reads and the alignments with fastqc and summarize the results with multiqc using the
fastqc_htmlandMultiqcmodules, respectively.
01.Assembly - Assemble Transcriptome using Trinity
Add_trinity_tags: Add tags required by trinity to the read titles /1 and /2 for forward and reverse reads, respectively. See Running-Trinity.
Assemble_Transcriptome: Assemble transcriptome with Trinity using the
trinitymodule.Rename_Transcripts: Rename transcripts by adding a prefix to their original names using the
Genericmodule. This is meant to facilitate data storage in a database management sytem like MySQL by generating analysis specific names for each transcript. No prefix is added by default.quastQC_full_transcriptome, BuscoQC_full_transcriptome: Assess the quality and completeness of the renamed transcriptome using quast and BUSCO, respectively.
02.Filtering - Filter out lowly expressed transcripts in two steps in order to select representative transcripts for annotation
Generate_Gene_Transcript_Map: Generate a gene to transcript mapping file by mapping the genes to thier respective isosforms with Trinity using the
trinity_mappingmodule.Map_reads_to_full_transcriptome: Map the quality checked trimmed reads to the assembled transcriptome using the gene to trancripts map in order to generate a count of reads per sample mappped to each gene or transcript by RSEM with Trinity using the
trinity_mappingmodule.Generate_count_matrix: Generate count or abundance matrices of both raw and normalized read counts per gene per sample by concatenating the counts per sample generated in the
Map_reads_to_full_transcriptomestep with Trinity usingtrinity_statisticsmodule. Statistics generated for these count matrices will then be used for the filteration step below.Filter_low_expressed_transcripts: Retain transcripts with at least x reads in at least n replicates in at least one treatment group using the
Genericmodule by running the R script “filter_trinity_by_counts.R”. Transcripts that pass this filtering step are referred to as the “filtered transcriptome” through out this documentation and in the parameter file. By default, we retain transcripts with at least 3 reads in at least 2 replicates or samples in a treatment group. You should adjust these parameters in order to meet your specific filtering criteria by passing the appropriate number to -M and -R parameters ofrun.sh.quastQC_filtered_transcripts and BuscoQC_filtered_transcripts: Assess the quality of the filtered transcriptome using quast and BUSCO as described above.
Make_filtered_transcripts_BLAST_db: Make a blast database from the filtered transcriptome using the
makeblastdbmodule to be uploaded to a blast server.Generate_filtered_Gene_Transcript_Map: Generate a gene to transcript mapping file of the filtered transcriptome by mapping the genes to thier respective isosforms with Trinity using the
trinity_mappingmodule.Map_reads_to_filtered_transcriptome: Map the quality checked trimmed reads to the filtered transcriptome using the gene to trancripts map in order to generate a count of reads per samplee mappped to each gene or transcript by RSEM with Trinity using the
trinity_mappingmodule.Generate_filtered_count_matrix: Generate count or abundance matrices of both raw and normalized read counts per gene per sample by concatenating the count per sample generated above with Trinity using
trinity_statisticsmodule.Select_representative_transcripts: Select representative transcripts with the Trinity script “filter_low_expr_transcripts.pl” with the –highest_iso_only parameter set to select the most highly expressed transcript per gene using the
Genericmodule. These representative transcripts will be used in sequence database searches for function prediction.quastQC_representative_transcripts and BuscoQC_representative_transcripts: Assess the quality and completeness of the representative transcripts using quast and BUSCO as described above.
03.Annotation - Annotate the representative trancript per gene
Split_representative_fasta: Split the fasta file of the representative transcripts to 1000 parts for parallelization when running blast using the
fasta_splittermodule. From this step onwards, analyses are performed on subsamples of the representative transcripts. Recombining the results is done in steps Merge_refseq_blastx_xmls and Merge_blast_results.- Prepare XML file for functional annotation using Blast2GO
Refseq_protein_blastx: Query the representative tanscripts with blastx against NCBI’s Refseq protein database using the
blastmodule and output the results in XML format.Merge_refseq_blastx_xmls: Merge the XML files produced in the previous step for the transcript subsamples in preparation for functional annotaton using Blast2GO with the python script “BlastXMLmerge.py” using the
Genericmodule. The Xml file generated from this step can then be export to Blast2GO desktop for function annotation.
- Using Trinotate
Generate_rep_Gene_Transcript_Map: Generate a gene to transcript mapping file of the representative trancripts by mapping the genes to thier respective trancripts with Trinity using the
trinity_mappingmodule.Swiss_prot_blastx: Query the representative transcripts with blastx against swissprot database using the
blastmodule.Identify_coding_region: Find coding sequences in the transcripts and produce predicted protein sequences using the
TransDecodermodule.Swiss_prot_blastp: Query translated representative transcripts with blastp against swissprot database using the
blastmodule.Identify_protein_domain: Run hmmscan against PFAM-A database with the translated representative transcript sequences using the
hmmscanmodule..Predict_rRNA: Run RNAMMER to predict rRNA sequences in the representative transcripts using the
RnammerTranscriptomemodule.Merge_protein_domain_results: Merge the hmmscan table produced in the
Identify_protein_domainstep for the transcript subsamples using themerge_tablesmodule.Merge_blast_results: Merge the blast tables produced in the previous steps for the transcript subsamples using the
merge_tablesmodule.Generate_annotation_table: Read the tables and produce the final annotation files i.e an excel annotation table and a sqlite database using the
Trinotatemodule.
- 04.Statistics - Statistical testing for differentially expressed genes and function enrichment analysis
- Statistical_analysis: Perform statistical testing for differential gene expression, clustering, and function enrichment analyses on the genes.result.txt files from the Map_reads_to_filtered_transcriptome step using the
DeSeq2module. Please see DeSeq2 tutorial for an indepth tutorial on how to customize the DeSeq2 module, its many functionalities and a description of the output files generated. The DeSeq2 module performs: Differential Gene Expression Using ‘DESeq2’ R Package
Gene Annotation from the Trinotate Results
Quality control eg. MA,Volcano and PCAs
Genes And Samples Filtering using ‘scater’ R package
Expression Patterns Clustering of Significant Genes
Clusters Visualization eg. Heatmaps and Trend Plots
Gene Ontology and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
Enrichment Analysis Visualization eg. Dot Plots
Gene Ontology and KEGG Terms Genes Overlap Visualization
Generates a Final Report in HTML Form per comparison.
- Statistical_analysis: Perform statistical testing for differential gene expression, clustering, and function enrichment analyses on the genes.result.txt files from the Map_reads_to_filtered_transcriptome step using the
Setting-up the conda environments
Get your organism specific ribosomal RNA sequences ready . To filter out ribosomal RNA sequences, download your organism’s ribosomal RNA sequences from NCBI, SILVA or any other rRNA database then pass the location of the sequences file to the -r option of configure.sh script described below. If a collection of ribosomal RNA reference sequences is unavailable for the organism of interest, you may retrieve relevant sequences from a broader taxonomic category (e.g. crustaceans) by searching NCBI Entrez with a search term like ribosomal rna[Title] OR rrna[Title] AND “Crustacea”[Organism]”.
Select your non-model organism’s BUSCO dataset from the list provided below and pass your choice to the -b flag of configure.sh and run.sh scripts below to download and install it.
- Bacteria
bacteria_odb9.tar.gz
proteobacteria_odb9.tar.gz
rhizobiales_odb9.tar.gz
betaproteobacteria_odb9.tar.gz
gammaproteobacteria_odb9.tar.gz
enterobacteriales_odb9.tar.gz
deltaepsilonsub_odb9.tar.gz
actinobacteria_odb9.tar.gz
cyanobacteria_odb9.tar.gz
firmicutes_odb9.tar.gz
clostridia_odb9.tar.gz
lactobacillales_odb9.tar.gz
bacillales_odb9.tar.gz
bacteroidetes_odb9.tar.gz
spirochaetes_odb9.tar.gz
tenericutes_odb9.tar.gz
- Eukaryota
eukaryota_odb9.tar.gz
fungi_odb9.tar.gz
microsporidia_odb9.tar.gz
dikarya_odb9.tar.gz
ascomycota_odb9.tar.gz
pezizomycotina_odb9.tar.gz
eurotiomycetes_odb9.tar.gz
sordariomyceta_odb9.tar.gz
saccharomyceta_odb9.tar.gz
saccharomycetales_odb9.tar.gz
basidiomycota_odb9.tar.gz
metazoa_odb9.tar.gz
nematoda_odb9.tar.gz
arthropoda_odb9.tar.gz
insecta_odb9.tar.gz
endopterygota_odb9.tar.gz
hymenoptera_odb9.tar.gz
diptera_odb9.tar.gz
vertebrata_odb9.tar.gz
actinopterygii_odb9.tar.gz
tetrapoda_odb9.tar.gz
aves_odb9.tar.gz
mammalia_odb9.tar.gz
euarchontoglires_odb9.tar.gz
laurasiatheria_odb9.tar.gz
embryophyta_odb9.tar.gz
protists_ensembl.tar.gz
alveolata_stramenophiles_ensembl.tar.gz
Run the one time environment configuration file configure.sh. To configure your environment, download
configure.sh, pass the required arguements i.e. the path to your rRNA sequences and your choice BUSCO dataset from the list above to the -r and -b options of the script, respectively. Please see the code examples below.# Download configure.sh and then make it executable wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/olabiyi/non-model_RNA_Seq/master/configure.sh && chmod +x configure.sh # If you don't have NeatSeq_Flow and Miniconda Installed run this line of code, # replacing "path/to/rRNA_sequences.fasta" with the correct path to your rRNA sequences. bash ./configure.sh -r path/to/rRNA_sequences.fasta -b metazoa_odb9.tar.gz >configure.log 2>&1 & # If you already have NeatSeq_Flow and Miniconda Installed run this line of code, # replacing "path/to/rRNA_sequences.fasta" with the correct path to your rRNA sequences. bash ./configure.sh -m 0 -n 0 -r path/to/rRNA_sequences.fasta -b metazoa_odb9.tar.gz >configure.log 2>&1 & # Monitor the installation tail -f configure.log
Running the pipeline on your data
Create a project directory and change into it. We call it
tutorialhere but you can give it any name you like.mkdir tutorial && cd tutorial
Get the your fastq data ready.
Get your neatseq flow formatted sample file ready. In the sample run below, we call it sample_data.nsfs but you can give it any name you like.
Content of sample_data.nsfs
Title project_title #SampleID Type Path Sample1 Forward raw_reads/Sample1_F1.fastq.gz Sample1 Forward raw_reads/Sample1_F2.fastq.gz Sample2 Forward raw_reads/Sample2_F1.fastq.gz Sample2 Reverse raw_reads/Sample2_R1.fastq.gz Sample3 Forward raw_reads/Sample3_F1.fastq.gz Sample3 Reverse raw_reads/Sample3_R1.fastq.gz Sample4 Forward raw_reads/Sample4_F1.fastq.gz Sample4 Reverse raw_reads/Sample4_R1.fastq.gz Sample5 Forward raw_reads/Sample5_F1.fastq.gz Sample5 Reverse raw_reads/Sample5_R1.fastq.gz Sample6 Forward raw_reads/Sample6_F1.fastq.gz Sample6 Reverse raw_reads/Sample6_R1.fastq.gz
Get your sample mapping file ready. In the sample run below, we call it sample_grouping.txt but you can give it any name you like.
Content of sample_grouping.txt
#SampleID Batch Treatment sample1 A PL_FD sample2 A PL_FD sample3 B PL_FD sample4 B PL_NFD sample5 C PL_NFD sample6 C PL_NFD
Run the pipeline
Automated run in one go at the commandline.
# Do this only once, just before your first run wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/olabiyi/non-model_RNA_Seq/master/run.sh && chmod +x run.sh # run this as many times as you want, each time specifying the parameters to the script as you please. Type ``./run.sh -h`` at the terminal for further help and options that can be passed to the script. # Run the whole pipeline bash ./run.sh -s sample_data.nsfs -m sample_grouping.txt -t transcript_prefix_ -b 'metazoa_odb9.tar.gz' -q bioinfo.q -g Treatment -n sge1027,sge1029,sge1030,sge1031,sge1032,sge1033,sge213,sge214,sge224,sge37,sge22 # Run only Refseq steps. By default the refseq steps are skipped because it takes a long time to complete. In order to run the refseq steps only after running the whole pipeline bash ./run.sh -s sample_data_body.nsfs -m sample_grouping_body.txt -t transcript_prefix_ -b metazoa_odb9.tar.gz -q bioinfo.q -g Treatment -n sge1027,sge1029,sge1030,sge1031,sge1032,sge1033,sge213,sge214,sge224,sge37,sge22 -T 99.reanalyze -r 1 -C Refseq_protein_blastx,99.reanalyze,Merge_refseq_blastx_xmls,99.reanalyze # Run a specific "Tag" or section. Here we run the ``04.Statistics`` section in order to perform only statistical and enrichment analysis. bash ./run.sh -s sample_data.nsfs -p non_model_RNA_Seq.yaml -m sample_grouping.txt -t transcript_prefix_ -b 'metazoa_odb9.tar.gz' -T 04.Statistics -q bioinfo.q -g Treatment -n sge1027,sge1029,sge1030,sge1031,sge1032,sge1033,sge213,sge214,sge224,sge37,sge22 # To Skip steps. Specify the step names to skip as a comma separated list to the -S option. bash ./run.sh -s sample_data.nsfs -m sample_grouping_body.txt -t transcript_prefix_ -b metazoa_odb9.tar.gz -q bioinfo.q -g Treatment -n sge1027,sge1029,sge1030,sge1031,sge1032,sge1033,sge213,sge214,sge224,sge37,sge22 -S Import_reads,QC_imported_reads,Trim_imported_reads,QC_trimmed_reads,SummarizeQC_imported_reads,SummarizeQC_trimmed_reads,Map_reads_to_rRNA,Filter_unmapped_reads,QC_unmapped_reads,SummarizeQC_unmapped_reads_and_alignment
Edit parameter file and run Neatseq_flow via the command line
# Dowload prepare_parmeter_file.sh and then make it executable wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/olabiyi/non-model_RNA_Seq/master/prepare_parameter_file.sh && chmod +x prepare_parameter_file.sh # Edit the parameter file automatically bash ./prepare_parameter_file.sh -s sample_data.nsfs -m sample_grouping.txt -t transcript_prefix_ -b 'metazoa_odb9.tar.gz' -q bioinfo.q -g Treatment -n sge1027,sge1029,sge1030,sge1031,sge1032,sge1033,sge213,sge214,sge224,sge37,sge22 # Run Neatseq flow # Download the run_neatseq_flow.sh script wget wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/olabiyi/non-model_RNA_Seq/master/run_neatseq_flow.sh && chmod +x run_neatseq_flow.sh # Run the whole pipeline bash ./run_neatseq_flow.sh -s sample_data.nsfs -m sample_grouping.txt -p non_model_RNA_Seq.yaml # Run a specific section ``-T`` of the pipeline. In the example quality check will only be perform. Type ./run_neatseq_flow.sh -h for usage information. bash ./run_neatseq_flow.sh -s sample_data.nsfs -m sample_grouping.txt -p non_model_RNA_Seq.yaml -T 00.Quality_check
Load edited paramater file into Neatseq flow GUI, edit even further then run via the GUI. For an indepth tutorial on how to use the GUI please see Neatseq flow GUI tutorial . Please note that unfortunately a parameter file that has been edited via the GUI cannot be run via the command line.
# Run only once bash source activate NeatSeq_Flow # Dowload prepare_parmeter_file.sh and then make it executable wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/olabiyi/non-model_RNA_Seq/master/prepare_parameter_file.sh && chmod +x prepare_parameter_file.sh # Edit the parameter file automatically ./prepare_parameter_file.sh -s sample_data.nsfs -m sample_grouping.txt -t Hippolyte3_ -b 'metazoa_odb9.tar.gz' -q bioinfo.q -g Treatment -n sge1027,sge1029,sge1030,sge1031,sge1032,sge1033,sge213,sge214,sge224,sge37,sge22 # Edit the parameter file "non_model_RNA_Seq.yaml" via the GUI NeatSeq_Flow_GUI.py
Monitor your work and view the output of each step in the
data/directory. In this directory, results are arranged in separate folders according to the neatseq flow module used to run the step. So to find the assembly from the the Assemble_Transcriptome step for example, navigate todata/trinity/Assemble_Transcriptome/. To know the module used for a particular step, please see the table A summary of steps in the pipeline above.# Run only once bash source activate NeatSeq_Flow # Run everytime you want to check the status of your work from your project directory neatseq_flow_monitor.py
Free-up some disk space (Optional)
# Download clean.sh (only once) wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/olabiyi/non-model_RNA_Seq/master/clean.sh # Free-up some disk space by deleting unnecessary files bash ./clean.sh
A brief introduction to conda
Conda is a powerful package and environment manager that you use with command line commands at the Anaconda Prompt for Windows, or in a terminal window for macOS or Linux. It allows you to have different versions of your programs installed in different environments without interfering with one another. In this way, you can have an environment with specific versions of all your programs installed and never have to worry that future changes to a required software will break your program. To view the programs installed in the non_model_RNA_Seq conda environment and their versions, type conda list at the terminal after running source activate non_model_RNA_Seq. For an indepth tutorial on conda, see conda tutorial .