NeatSeq-Flow modules
Module categories
Preparation and QC
Modules included in this section
Import *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for importing and merging files from the sample file into NeatSeq-Flow.
Files can be imported in three ways:
If there is a single file in the type (per sample), it can be imported, i.e. the exiting file path will be used as source for the workflow.
If there are multiple files in the type, or you would like to make a local copy of the raw files, the file(s) can be copied and concatenated to the workflow directory.
If the raw files are compressed, importing can include decompression as well as concatenation.
Tip
If you have plenty of disk space, the 2nd and 3rd options are the recommended approach. It ensures the original files go untouched and when the workflow is complete you can discard the copies produced by NeatSeq-Flow.
The Import module can be used in two modes:
- The Basic mode
NeatSeq-Flow will attempt to guess all the parameters it requires. Multiple files will be concatenated and stored in the file type index according to the table below. File types not included in the table will be stored in the file type index by the type specified in the sample file.
You have to make sure that all files of each file type have the same extension for NeatSeq-Flow to guess the
script_pathandpipeparameters.- The Advanced mode
is used when more control on data importing and concatenation is required. It enables full control over which file types are imported, how they are copied and in which slots they are placed in the file type index. It also enables importing file types not recognized by NeatSeq-Flow (see list below).
In this mode, you have to define the following lists:
src,trg,script_path,scopeandext. For each file type in the sample file, you should have an entry in thesrclist. The other lists should apply to the equivalent entry insrc.trgis the target file type (in the file type index) for the imported files,script_pathis the shell command to use to concatenate the source type files,scopeis the scope for which the source type is defined andextis the suffix to append to the final filenames. Strings are expanded to the length ofsrclist, so ifscript_pathis the same for all source types, it is enough to specify it once.When using the Advanced mode, by passing the
srclist, you must also define the other lists, i.e.trg,ext,scopeandscript_path. However, NeatSeq-Flow will try guessing the lists based on the lists of recognized file types and extensions.If some of the file types in
srcare recognized and some are not, you can pass the lists mentioned above with values for the unrecognized types, leaving null in the positions of the recognized types. These null values will be guessed by NeatSeq-Flow.The advanced mode is experimental, and documentation will hopefully improve as we gain experience with it.
Note
- Definition of
script_pathin theimportmodule script_pathshould be a shell program that receives a list of files and produces one single output file to the standard error. Examples of such programs arecatfor text files andgzip -cdfor gzipped files. Other types of compressed files should have such a command as well.
Tip
NeatSeq-Flow attempts to guess the script_path and pipe values based on the input file extensions. For this to work, leave the script_path and pipe lists empty and make sure all files from the same source have the same extensions (e.g. all gzipped files should have .gz as file extension).
If you want NeatSeq-Flow to guess only some of the script_path values, set them to null or to ..guess.., e.g. if src is [Single,TYP1] and script_path is [null,cat], then the script_path for Single will be guessed and the script_path for TYP1 will be set to cat.
Two more options are available for script path: ..skip.. will skip the type entirely, while ..import.. will import the values from the sample file into the relevant slots without actually producing any scripts (This is useful for including entities which are not files in the sample file. e.g. in the qiime2 pipeline you might want to include a semantic type in the sample file).
The following extensions are recognized:
Extension |
|
|
|---|---|---|
.fasta |
cat |
|
.faa |
cat |
|
.fna |
cat |
|
.txt |
cat |
|
.tsv |
cat |
|
.csv |
cat |
|
.fastq |
cat |
|
.fa |
cat |
|
.fq |
cat |
|
.gz |
gzip -cd |
|
.zip |
echo |
‘xargs -d ” ” -I % sh -c “unzip -p %”’ |
.bz2 |
bzip -cd |
|
.dsrc2 |
echo |
‘xargs -d ” ” -I % sh -c “dsrc2 d -s %”’ |
.dsrc |
echo |
‘xargs -d ” ” -I % sh -c “dsrc d -s %”’ |
Requires
- For the basic mode:
A list of files of the following types, either in
[<sample>]or in[project_data]:
Source |
Target |
|---|---|
Forward |
fastq.F |
Reverse |
fastq.R |
Single |
fastq.S |
Nucleotide |
fasta.nucl |
Protein |
fasta.prot |
SAM |
sam |
BAM |
bam |
REFERENCE |
reference |
VCF |
vcf |
G.VCF |
g.vcf |
GTF |
gtf |
GFF |
gff |
GFF3 |
gff3 |
manifest |
qiime2.manifest |
barcodes |
barcodes |
- For the Advanced mode:
Lists of files in any file type, either in
[<sample>]or in[project_data].
Output
Imported files of the types in the table above are placed in slots according to the types in the 2nd column of the table.
Attention
If you want to do something more complex with the combined files, you can use the pipe parameter to send extra commands to be piped on the files after the main command. This is an experimental feature and should be used with care.
e.g.: You can get files from a remote location by setting script_path to curl and pipe to gzip -cd. This will download the files with curl, unzip them and concatenate them into the target file. In the sample file, specify remote URLs instead of local pathes. This will work only for one file per sample.
As of version 1.3.0, pipe can be a list of the same length as src and it we be treated like the other lists describe above.
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
script_path |
The shell command to use for merging the source files. |
|
src |
A list of source file types as the appear in the sample file. |
|
trg |
A list of target file type for the imported files. |
|
scope |
sample | project |
The scope at which each of the sources can be found. |
ext |
The suffix to append to the imported filename. |
|
pipe |
Additional commands to be piped on the files before writing to file. |
Lines for parameter file
Basic mode, gzipped files:
import1:
module: Import
script_path: gzip -cd
Basic mode, remote files:
Import1:
module: Import
script_path: curl
pipe: gzip -cd
Advanced mode, mixture of types and scopes:
Import1:
module: Import
src: [UR1, UR2]
script_path: [gzip -cd, cat]
scope: [sample, project]
trg: [unrecog1, unrecog2]
ext: [ur1, ur2]
Advanced mode, both recognized and unrecognized file types:
Import1:
module: Import
src: [UR1, Forward, Reverse]
script_path: [gzip -cd, null, null]
scope: # Guess!
trg: [unrecog1, null, null]
ext: [ur1, null, null]
Advanced mode, same types in samples and project:
Import1:
module: Import
src: [Nucleotide, Nucleotide]
script_path: [cat, cat]
scope: [sample, project]
trg:
ext:
fastqc_html *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running fastqc.
Creates scripts that run fastqc on all available fastq files.
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
puts fastqc output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastqc_fastq.F_html"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastqc_fastq.R_html"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastqc_fastq.S_html"]
puts fastqc zip files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastqc_fastq.F_zip"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastqc_fastq.R_zip"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastqc_fastq.S_zip"]
Lines for parameter file
fqc_merge1:
module: fastqc_html
base: merge1
script_path: /path/to/FastQC/fastqc
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 15
redirects:
--threads: 15
References
Andrews, S., 2010. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data.
trimmo *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running trimmomatic on fastq files
Requires
fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
puts fastq output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"|"fastq.R"|"fastq.S"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
spec_dir |
path |
If trimmomatic must be executed within a particular directory, specify that directory here |
todo |
LEADING:20 TRAILING:20 |
The trimmomatic arguments |
Lines for parameter file
trim1:
module: trimmo
base: merge1
script_path: java -jar trimmomatic-0.32.jar
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
node: node1
spec_dir: /path/to/Trimmomatic_dir/
todo: LEADING:20 TRAILING:20
redirects:
-threads: 20
References
Bolger, A.M., Lohse, M. and Usadel, B., 2014. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics, 30(15), pp.2114-2120.
Multiqc *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for preparing a MultiQC report for all samples.
Tip
By default, the module will search for parsable reports in the directories of all the modules in the branch leading to this instance. To search only in the directories of the explicit base steps, specify the bases_only parameter.
Requires
No real requirements. Will give a report with information if one of the base steps produces reports that MultiQC can read, e.g. fastqc, bowtie2, samtools etc.
Output
puts report dir in the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["Multiqc_report"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
bases_only |
Search directories of explicit base steps only. |
Lines for parameter file
firstMultQC:
module: Multiqc
base:
- sam_bwt2_1
- fqc_trim1
bases_only:
script_path: /path/to/multiqc
References
Ewels, P., Magnusson, M., Lundin, S. and Käller, M., 2016. MultiQC: summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics, 32(19), pp.3047-3048.
Cutadapt
- Authors
Levin Liron
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Short Description
A module for running cutadapt on fastqc files
Requires
- fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
- puts fastq output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Cutadapt # Name of the module used
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a merge step]
script_path: # Command for running the Cutadapt script
paired: # Analyse Forward and Reverse reads together.
Demultiplexing: # Use to Demultiplex the adaptors, needs to be in the format of name=adaptor_seq
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
redirects:
--too-short-output: # will replace @ with the location of the sample dir [e.g. @too_short.fq]
-a: # Use to trim poly A in SE reads [e.g. "A{100} -A T{100}"]
References
Martin, Marcel. “Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads.” EMBnet. journal 17.1 (2011): pp-10
Trim_Galore
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Short Description
A module for running Trim Galore on fastq files
Requires
- fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
- puts fastq output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
- puts unpaired fastq output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F.unpaired"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R.unpaired"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Comments
- This module was tested on:
Trim Galore v0.4.2Cutadapt v1.12.1
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Trim_Galore # Name of the module used
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a merge step]
script_path: # Command for running the Trim Galore script
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
cutadapt_path: # Location of cutadapt executable
redirects:
--length: # Parameters for running Trim Galore
-q: # Parameters for running Trim Galore
References
- Cutadapt:
Martin, Marcel. “Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads.” EMBnet journal 17.1 (2011):pp-10
- Trim Galore:
Krueger F: Trim Galore. [http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/]
fastq_screen
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for executing fastq_screen on sequence files.
Input files are specified with the type parameter or taken from the fastq slots, one script per fastq file.
In regular mode, no output file are produced. However, if the --tag is included, the tagged file will be stored in the equivalent fastq.X slot.
If a --filter tag is included, the filtered file will be stored in the equivalent fastq.X slot.
The parameters can be passed through a configuration file specified in the redirected parameters with the --conf parameter.
Alternatively, if you do not specify the configuration file, one will be produced for you. For this, you must include:
A
genomessection specifying genome indices to screen against (see examples below) andan
alignersection specifying the aligning program to use and it’s path.
Additionally, if a --threads parameter is included in the redirects, it will be incorporated into the configuration file.
Attention
If a --bisulfite redirected parameter is included, it should contain the path to Bismark, which will be included in the configuration file.
Requires
fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
If
--tagand/or--filteror--nohitsare included, puts output fastq files in:sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genomes |
|
If |
aligner |
|
If |
Lines for parameter file
No configuration file:
fastq_screen:
module: fastq_screen
base: merge1
script_path: {Vars.paths.fastq_screen}
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 60
aligner:
bowtie2: {Vars.paths.bowtie2}
genomes:
Human: {Vars.databases.human}
Mouse: {Vars.databases.moiuse}
PhiX: {Vars.databases.phix}
redirects:
--filter: 200
--tag:
# --nohits:
--force:
--threads: 60
With configuration file:
fastq_screen:
module: fastq_screen
base: merge1
script_path: {Vars.paths.fastq_screen}
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 60
redirects:
--conf: {Vars.paths.fastq_screen_conf_file}
--filter: 200
--tag:
# --nohits:
--force:
References
Wingett, S.W. and Andrews, S., 2018. FastQ Screen: A tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control. F1000Research, 7.
Mapping
Modules included in this section
bowtie2_builder *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running bowtie2 index builder:
Builds a bowtie2 index for a fasta file stored at the project or sample level.
Determine which one will be used by specifying scope as either project or sample.
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
- Puts output index files in one of the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["bowtie2.index"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["bowtie2.index"]
- Puts the fasta file in the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["reference"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project fasta or a sample fasta. |
Lines for parameter file
bwt2_build:
module: bowtie2_builder
base: trinity1
script_path: /path/to/bowtie2-build
scope: project
References
Langmead, B. and Salzberg, S.L., 2012. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nature methods, 9(4), pp.357-359.
bowtie2_mapper *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running bowtie2 mapper:
The reads stored in each sample are aligned to one of the following bowtie2 indices:
An external index passed with the
-xparameter.A bowtie2 index on a project fasta files, such as an assembly from all samples. Specify with
bowtie2_mapper:scope projectA sample bowtie2 index on a sample-specific fasta file, such as from a sample-wise assembly or from the sample file. Specify with
bowtie2_mapper:scope sample
The latter two options must come after a bowtie2_builder instance.
Tip
See the documentation for the bowtie2_builder module.
Note
fastq files are never defined project-wide
The scope parameter controls the origin of the index files, i.e. wheather the fasta file to map to is an assembly of the sample reads (scope: sample) or an assembly of all reads in the project (scope: project). The reads to be mapped are always saple reads, as a ‘fastq’ slot is not defined at the project level.
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
- Puts output sam files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
- Puts the name of the mapper in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["mapper"]
- puts fasta of reference genome (if one is given in param file) in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["reference"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
-x |
path to bowtie2 index |
If not given, will look for a project bowtie2 index and then for a sample bowtie2 index |
ref_genome |
path to genome fasta |
If -x is NOT given, will use the equivalent internal fasta. If -x is passed, and ref_genome is NOT passed, will leave the reference slot empty |
get_map_log |
Store the log produced by bowtie2 (This is bowtie2 standard output) |
|
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project or sample bowtie2 index. |
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
bwt2_1:
module: bowtie2_mapper
base: trim1
script_path: /path/to/bowtie2
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
get_map_log:
ref_genome: /path/to/ref_genome.fna
redirects:
-p: 20
-q: null
-x: /path/to/bowtie2.index/ref_genome
Using a bowtie2 index constructed from a project fasta:
bwt2_1:
module: bowtie2_mapper
base: bwt2_bld1
script_path: /path/to/bowtie2
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
get_map_log:
scope: project
redirects:
-p: 20
-q: null
References
Langmead, B. and Salzberg, S.L., 2012. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nature methods, 9(4), pp.357-359.
bowtie1_builder *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running bowtie1 index builder:
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
output
- Puts output index files in one of the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["bowtie1.index"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["bowtie1.index"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
path to bowtie1 index |
If not given, will look for a project bowtie1 index and then for a sample bowtie1 index |
Lines for parameter file
bwt1_bld_ind:
module: bowtie1_builder
base: trinity1
script_path: /path/to/bowtie
scope: project
References
Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M. and Salzberg, S.L., 2009. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome biology, 10(3), p.R25.
bowtie1_mapper *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running bowtie1 mapper:
The reads stored in each sample are aligned to one of the following bowtie indices:
An external index passed with the
ebwtparameter.A bowtie index on a project fasta files, such as an assembly from all samples. Specify with
bowtie1_mapper:scope projectA sample bowtie1 index on a sample-specific fasta file, such as from a sample-wise assembly or from the sample file. Specify with
bowtie1_mapper:scope sample
The latter two options must come after a bowtie1_builder instance.
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
- Puts output sam files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
- Puts the name of the mapper in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["mapper"]
- Puts fasta of reference genome (if one is given in param file) in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["reference"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
ebwt |
path to bowtie1 index |
If not given, will look for a project bowtie1 index and then for a sample bowtie1 index |
ref_genome |
path to genome fasta |
If ebwt is NOT given, will use the equivalent internal fasta. If ebwt IS given, and ref_genome is NOT passed, will leave the reference slot empty. |
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project or sample bowtie1 index. |
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
bwt1:
module: bowtie1_mapper
base: trim1
script_path: /path/to/bowtie
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
ebwt: /path/to/bowtie1.index/ref_genome
ref_genome: /path/to/ref_genome.fna
redirects:
-p: 20
For project bowtie index:
bwt1_1:
module: bowtie1_mapper
base: bwt1_bld_ind
script_path: /path/to/bowtie
scope: project
References
Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M. and Salzberg, S.L., 2009. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome biology, 10(3), p.R25.
bwa_builder *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running bwa index builder:
Builds a bwa index for a fasta file stored at the project or sample level.
Determine which one will be used by specifying scope as either project or sample.
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
- Puts output index files in one of the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["bwa_index"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["bwa_index"]
- Puts the fasta file in one of the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["reference"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project fasta or a sample fasta. |
Lines for parameter file
bwa_bld_ind:
module: bwa_builder
base: spades1
script_path: /path/to/bwa index
scope: project
References
Li, H. and Durbin, R., 2009. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics, 25(14), pp.1754-1760.
bwa_mapper *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running bwa mapper:
The reads stored in each sample are aligned to one of the following bwa indices:
An external index passed with the
ref_indexparameter.A bwa index on a project fasta files, such as an assembly from all samples. Specify with
bwa_mapper:scope projectA sample bwa index on a sample-specific fasta file, such as from a sample-wise assembly or from the sample fasta file. Specify with
bwa_mapper:scope sample
The latter two options must come after a bwa_builder instance.
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
- If
modis one ofsamse, sampe, the sai files are required as well (created by abwa alnstep: self.sample_data[<sample>]["saiF|saiR|saiS"]
- If
Output
- Puts output sam files in the following slots:
- If
modis one ofmem, samse, sampe, bwasw: self.sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
- If
- If
modisaln: self.sample_data[<sample>]["saiF|saiR|saiS"]
- If
- Puts the name of the mapper in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["mapper"]
- puts fasta of reference genome (if one is given in param file) in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["reference"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
ref_index |
path to bwa index |
If not given, will look for a project bwa index and then for a sample bwa index |
ref_genome |
path to genome fasta |
If ref_index is NOT given, will use the equivalent internal fasta. If ref_index is passed, and ref_genome is NOT passed, will leave the reference slot empty |
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project or sample bwa index. |
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
Using
mem:
bwa_mem_1:
module: bwa_mapper
base: trim1
script_path: /path/to/bwa
mod: mem
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
ref_genome: /path/to/ref_genome.fna
ref_index: /path/to/bwa_index/ref_genome
redirects:
-t: 20
2. Using ``aln - samse/sampe``:
bwa_aln_1:
module: bwa_mapper
base: trim1
script_path: /path/to/bwa_mapper
mod: aln
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
ref_genome: /path/to/ref_genome.fna
ref_index: /path/to/bwa_index/ref_genome
redirects:
-t: 20
bwa_samse_1:
module: bwa_mapper
base: bwt2_1
script_path: /path/to/bwa
mod: samse
ref_genome: /path/to/ref_genome.fna
ref_index: /path/to/bwa_index/ref_genome
For project bwa index:
bwa_1:
module: bwa_mapper
base: bwa_bld_ind
script_path: /path/to/bwa
mod: mem
scope: project
References
Li, H. and Durbin, R., 2009. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics, 25(14), pp.1754-1760.
STAR_mapper
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running STAR mapper:
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
If
scopeis set (must come afterSTAR_buildermodule which populates the required slots):STAR index directories in:
sample_data[<sample>]["STAR.index"]ifscope= “sample”sample_data["STAR.index"]ifscope= “project”
Reference fasta files in:
sample_data[<sample>]["STAR.fasta"]ifscope= “sample”sample_data["STAR.fasta"]ifscope= “project”
Output
Puts output sam files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
Alternatively, if
--outSAMtypeis set toBAM, puts output BAM files in the following slots:self.sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["bam_unsorted"]
High confidence collapsed splice junctions (SJ.out.tab file) will be stored in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["SJ.out.tab"]
If
--quantModecontainsTranscriptomeSAM, alignments BAM translated into transcript coordinates will be stored in:self.sample_data[<sample>]["TranscriptomeSAM"]
If
--quantModecontainsGeneCounts, theReadsPerGene.out.tabfile will be stored:self.sample_data[<sample>]["GeneCounts"]
If
--outWigTypeis set, will store outputs in:if
--outWigTypeiswiggleself.sample_data[<sample>]["wig2_UniqueMultiple"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["wig2_Unique"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["wig1_UniqueMultiple"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["wig1_Unique"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["wig"]
if
--outWigTypeisbedGraphself.sample_data[<sample>]["bdg2_UniqueMultiple"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["bdg2_Unique"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["bdg1_UniqueMultiple"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["bdg1_Unique"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["bdg"]
- Puts the name of the mapper in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["mapper"]
- Puts fasta of reference genome (if one is given in param file) in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["reference"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
ref_genome |
path to genome fasta |
|
scope |
project | sample |
The scope from which to take the genome directory |
Note
You can set the RG atrribute of the resulting SAM/BAM files with the redirected parameter --outSAMattrRGline
This will set the equivalent STAR parameter.
By default, the parameter will be set to include ID and SM tags, both set to the sample name. You can set the SM tag, but any ID tags will be removed and replaced with the sample name.
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
STAR_map:
module: STAR_mapper
base: STAR_bld_ind
script_path: /path/to/STAR
redirects:
--readMapNumber: 1000
--genomeDir: /path/to/genome/STAR_index/
For project STAR index:
STAR_map:
module: STAR_mapper
base: STAR_bld_ind
script_path: /path/to/STAR
scope: project
redirects:
--readMapNumber: 1000
References
Dobin, A., Davis, C.A., Schlesinger, F., Drenkow, J., Zaleski, C., Jha, S., Batut, P., Chaisson, M. and Gingeras, T.R., 2013. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics, 29(1), pp.15-21.
STAR_builder
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running STAR genome index construction:
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
If
--sjdbGTFfileis set in redirects, but left empty, will expect to find aGTFfile here:sample_data["gtf"]ifscope= “project”sample_data[<sample>]["gtf"]ifscope= “sample”
If
--sjdbFileChrStartEndis set in redirects, but left empty, will expect to find an SJ file here:sample_data["SJ.out.tab"]ifscope= “project”sample_data[<sample>]["SJ.out.tab"]ifscope= “sample”
Output
Puts output index files in one of the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["STAR.index"]
self.sample_data["project_data"]["STAR.index"]
Puts the reference fasta file in one of the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["STAR.fasta"]
self.sample_data["project_data"]["STAR.fasta"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
Not used |
Lines for parameter file
STAR_bld_ind:
module: STAR_builder
base: trinity1
script_path: /path/to/STAR
scope: project
qsub_params:
queue: star.q
redirects:
--genomeSAindexNbases: 12
--genomeChrBinNbits: 10
References
Dobin, A., Davis, C.A., Schlesinger, F., Drenkow, J., Zaleski, C., Jha, S., Batut, P., Chaisson, M. and Gingeras, T.R., 2013. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics, 29(1), pp.15-21.
STAR_LoadRemoveGenome
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for loading a STAR genome into RAM for use by subsequent STAR mapping jobs.
Note
This module saves memory and time. Set parameter --genomeLoad in the STAR mapping instance to LoadAndKeep.
This will load the genome once into memory and use it repeatedly for all instances executed on the same node.
When all mapping jobs are completed, Scripts produced by this instance will remove the genome from RAM for all
nodes used.
Tip
Make sure you set the node parameter in qsub_params to all the nodes in use by the base STAR_mapper instance.
Attention
Currently defined for project-scope or external genomes only. Not used for sample-scope genomes.
Note
Loading a genome is not really required. It will be loaded by the first instance of STAR.
Requires
A STAR genome in:
sample_data["STAR.index"]
Alternatively, a STAR genome index can be passed with the --genomeDir parameter.
Output
No output is created
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome |
load|remove |
Load or remove genome from RAM |
qsub_params:node |
Nodes on which to load/unload genome |
|
scope |
project | sample |
The scope from which to take the genome directory. Currently not in use |
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
STAR_remove_genome:
module: STAR_LoadRemoveGenome
base: STAR_map
script_path: '{Vars.paths.STAR}STAR'
genome: remove
qsub_params:
queue: queue.q
node: {Vars.nodes}
redirects:
--genomeDir: /path/to/STAR/genome_directory
For project STAR index:
STAR_remove_genome:
module: STAR_LoadRemoveGenome
base: STAR_map
script_path: '{Vars.paths.STAR}STAR'
genome: remove
qsub_params:
queue: queue.q
node: {Vars.nodes}
References
Dobin, A., Davis, C.A., Schlesinger, F., Drenkow, J., Zaleski, C., Jha, S., Batut, P., Chaisson, M. and Gingeras, T.R., 2013. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics, 29(1), pp.15-21.
samtools *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for executing samtools on a SAM or BAM file.
Warning
This module is in beta stage. Please report issues and we’ll try solving them
Attention
The module was tested on samtools 1.9
Currently, the samtools programs included in the module are the following:
viewsortindexflagstatstatsidxstatsdepthfastq/amergempileup
Note
Order of samtools subprogram execution
The
samtoolsprograms are executed in the order given in the parameter fileFile types are passed from one program to the next
In order to execute one program more than once, append digits to the program name, e.g.
sort2,index3etc.
Arguments can be passed to the tools following the program name in the parameter file, e.g.:
sort: -n -@ 10
Alternatively, they can be passed in a redirects block:
sort:
redirects: -n -@ 10
Please do NOT pass input and output arguments - they are set by the module.
Some of the tools are defined only when the scope is sample:
mergemerges the sample-wise BAM files into a project BAM file.mpileupcreates a project VCF/BCF/mpileup file from the sample BAM files.
Attention
Treatment of regions
If you want to limit the program to a specific region, pass the program name a block with a ‘region’ section. If you want to set the region and pass some redirects, add a ‘redirects’ section as well. For example:
mpileup:
redirects: --max-depth INT -v
region: chr2:212121-32323232
Attention
Treatment of BED files
In samtools view, bedcov, depth and mpileup, you can pass a BED file by adding a bed field in the tool block, with one of the following values:
sample- use a sample-scope BED fileproject- use a project-scope BED fileA full path to a BED file.
Example:
view:
redirects: -uh -q 30 -@ 20 -F 4
bed: /path/to/external/bed
Requires
A SAM file in the following location:
sample_data[<sample>]["sam"](forscope=sample)sample_data["project_data"]["sam"](forscope=project)
Or a BAM file in:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"](forscope=sample)sample_data["project_data"]["bam"](forscope=project)
Note
If both BAM and SAM files exist, select the one to use with type2use (see section Parameters that can be set).
Output
Depending on the parameters, will put files in different types (e.g. bam, cram, sam, bam, bai, crai, vcf, bcf, mpileup, fasta.{F,R,S}, fastq.{F,R,S})
Please use stop_and_show to see the types produced by your instance of samtools_new.
Note
If scope is set to project, the above mentioned output files will be created in the project scope.
Note
merge and mpileup are only defined when scope is sample. See above
By default, all files are saved. To keep only the output from specific programs, add a keep_output section containing a list of programs for which the output should be saved. All other files will be discarded.
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
project |
sample|project |
Scope of SAM/BAM top operate on. Defaults to |
view |
e.g.: -buh -q 30 |
|
sort |
e.g.: -@ 20 |
|
index |
|
|
flagstat |
Leave empty. flagstat takes no parameters |
|
stats |
|
|
idxstats |
|
|
fastq/a |
|
|
merge |
|
|
region |
A region to limit the region-limitable programs, such as |
|
type2use |
sam|bam |
Type of file to use. Must exist in scope |
keep_output |
[sort, view, sort2] |
A list of programs for which to store the output files. By deafult, all files are saved. |
Lines for parameter file
sam_bwt1:
module: samtools_new
base: bwt1
script_path: {Vars.paths.samtools}
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
region: chr2:212121-32323232
scope: sample
# First 'view'. Use FLAG to filter alignments:
view: -uh -q 30 -@ 20 -F 4 -O bam
# First 'sort'. Sort by coordinates:
sort: -@ 20
# Second 'view'. Use region to filter alignments:
view2:
redirects: -buh -q 30 -@ 20
region: chr2:212121-32323232
index:
flagstat:
stats: --remove-dups
idxstats:
# Second 'sort'. Sort by name:
sort2: -n -@ 20
# Get sequences from name-sorted BAM file:
fastq:
# Merge BAM name sorted BAM files
merge:
region: chr2:212121-32323232
# Create VCF from Merge BAM name sorted BAM files
mpileup:
redirects: --max-depth INT -v
region: chr2:212121-32323232
keep_output: [sort, view, index, flagstat, stats, fastq, mpileup, merge]
# stop_and_show:
References
Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., Fennell, T., Ruan, J., Homer, N., Marth, G., Abecasis, G. and Durbin, R., 2009. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics, 25(16), pp.2078-2079.
Multiqc *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for preparing a MultiQC report for all samples.
Tip
By default, the module will search for parsable reports in the directories of all the modules in the branch leading to this instance. To search only in the directories of the explicit base steps, specify the bases_only parameter.
Requires
No real requirements. Will give a report with information if one of the base steps produces reports that MultiQC can read, e.g. fastqc, bowtie2, samtools etc.
Output
puts report dir in the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["Multiqc_report"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
bases_only |
Search directories of explicit base steps only. |
Lines for parameter file
firstMultQC:
module: Multiqc
base:
- sam_bwt2_1
- fqc_trim1
bases_only:
script_path: /path/to/multiqc
References
Ewels, P., Magnusson, M., Lundin, S. and Käller, M., 2016. MultiQC: summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics, 32(19), pp.3047-3048.
RSEM
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Short Description
A module for running RSEM
Requires
- fastq file in
self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.F"]self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.R"]self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.S"]
- or bam file in
self.sample_data[sample]["bam"]
Output
- puts output bam files (if the input is fastq) in:
self.sample_data[sample]["bam"]
- puts the location of RSEM results in:
self.sample_data[sample]["RSEM"]self.sample_data[sample]["genes.results"]self.sample_data[sample]["isoforms.results"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
mode |
transcriptome/genome |
Is the reference is a genome or a transcriptome? |
gff3 |
None |
Use if the mode is genome and the annotation file is in gff3 format |
Comments
- This module was tested on:
RSEM v1.2.25bowtie2 v2.2.6
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: RSEM # Name of the module used
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a bam file generator step or merge with fastq files]
script_path: # Command for running the RSEM script
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
mode: # transcriptome or genome
export_transcriptome: # In genome mode set the extracted transcriptome as the new project level fasta.nucl and extract the ranscript-to-gene-map file as project level gene_trans_map
annotation: # For Genome mode: the location of GTF file [the default] , for GFF3 use the gff3 flag. For Transcriptome mode: transcript-to-gene-map file.
# If annotation is set to Trinity the transcript-to-gene-map file will be generated using the from_Trinity_to_gene_map script
# If not set will use only the reference file as unrelated transcripts
from_Trinity_to_gene_map_script_path: # If the mode is transcriptome and the reference was assembled using Trinity it is possible to generate the transcript-to-gene-map file automatically using this script
# If annotation is set to Trinity and this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
gff3: # Use if the mode is genome and the annotation file is in gff3 format
mapper: # bowtie/bowtie2/star
mapper_path: # Location of mapper script
rsem_prepare_reference_script_path: # Location of preparing reference script
plot_stat: # Generate statistical plots
plot_stat_script_path: # Location of statistical plot generating script
reference: # The reference genome/transcriptome location [FASTA file]
rsem_generate_data_matrix_script_path: # Location of the final matrix generating script
# If this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
redirects:
--append-names: # RSEM will append gene_name/transcript_name to the result files
--estimate-rspd: # Enables RSEM to learn from the data how the reads are distributed across a transcript
-p: # Number of CPUs to use in this analysis
--bam: # Will use bam files and not fastq
--no-bam-output:
--output-genome-bam: # Alignments in genomic coordinates (only if mode is genome)
References
Li, Bo, and Colin N. Dewey. “RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome.” BMC bioinformatics 12.1 (2011): 323.
htseq_count
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running htseq-count:
See htseq-count documentation.
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
Output
- Puts the output file in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["HTSeq.counts"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
gff |
path to bowtie1 index |
If not given, will look for a project bowtie1 index and then for a sample bowtie1 index |
-f|–format |
sam | bam |
In redirects. Tells htseq-count which file to use. If not specified, will use whichever file exists. |
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
htseq_c1:
module: htseq_count
base: samtools_STAR1
script_path: /storage16/app/bioinfo/python_packages/bin/htseq-count
gtf: /fastspace/bioinfo_databases/STAR_GRCh38_Gencode21/gencode.v21.annotation.gtf
redirects:
--format: bam
-s: 'no'
-m: intersection-nonempty
References
Anders, S., Pyl, P.T. and Huber, W., 2015. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics, 31(2), pp.166-169.
RSEM_prep
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running rsem-prepare-reference:
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"](scope=project)sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"](scope=sample)
If neither exists, please supply
referenceparameter.
Attention
If type “gene_trans_map” exists, its value will be used for “–transcript-to-gene-map”, unless “–transcript-to-gene-map” is explicitly passed in redirects!
Output
Puts output index files in one of the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["RSEM.index"]
self.sample_data["project_data"]["RSEM.index"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
Where to take the reference from |
reference |
path to reference |
Use this fasta file. See the definition for reference_fasta_file(s) in the ARGUMENTS section of rsem-prepare-reference help |
Lines for parameter file
RSEM_prep_ind:
module: RSEM_prep
base: merge1
script_path: /path/to/RSEM
reference: /path/to/fasta
redirects:
--gtf: /path/to/gtf
--transcript-to-gene-map: /path/to/map_file
References
RSEM_mapper
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running rsem-calculate-expression:
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"](scope=project)sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"](scope=sample)
If neither exists, please supply
referenceparameter.
Output
Puts output index files in one of the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["genes.counts"]
self.sample_data[<sample>]["isoforms.counts"]
And the following BAMs, depending on redirected params:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["genome.unsorted.bam"]
self.sample_data[<sample>]["genome.bam"]
self.sample_data[<sample>]["transcript.unsorted.bam"]
self.sample_data[<sample>]["transcript.bam"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
The scope of the RSEM index. Must match the scope in the RSEM_prep instance. |
result2use |
genes | isoforms |
Summarize counts at the gene or isoform level. |
Lines for parameter file
Mapping fastq files:
RSEM_map:
module: RSEM_mapper
base: merge1
script_path: {Vars.paths.RSEM.rsem-calculate-expression}
reference: /path/to/fasta
redirects:
--gtf: /path/to/gtf
--transcript-to-gene-map: /path/to/map_file
Parsing an existing BAM alignment file:
RSEM_parse_bam:
module: RSEM_mapper
base: mv_transcript_bam_to_bam
script_path: {Vars.paths.RSEM.rsem-calculate-expression}
scope: project
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
redirects:
--num-threads: 20
References
BAM Conversion to Other Formats
Modules included in this section
genomeCoverageBed *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running bedtools genomecov:
The module builds a bedgraph (bdg) file based on an existing BAM file.
Requires
BAM file in the following slot:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]
Output
- Puts output BedGraph files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["bdg"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
-g |
path to chrom.sizes |
You must redirect the -g parameter. Create the chrom.sizes file for the reference genome with |
Lines for parameter file
genCovBed_bwt1:
module: genomeCoverageBed
base: sam_bwt1
script_path: /path/to/bedtools/bin/genomeCoverageBed
redirects:
-bg:
-g: /path/to/ref_genome/ref_genome.chrom.sizes
References
UCSC_BW_wig
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for creating wig and bigwig files using UCSC tools:
The module creates bigwig and wig files from the current active BedGraph file.
Requires
BedGraph file in the following slot:
sample_data[<sample>]["bdg"]
Output
Puts output sam files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>][“bw”]
self.sample_data[<sample>][“wig”]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
bedGraphToBigWig_params |
e.g. -blockSize=10 -itemsPerSlot=20 |
Parameters to pass to |
bigWigToWig_params |
e.g. -chrom X1 -start X2 -end X3 |
Parameters to pass to |
script_path |
Path to dir where UCSC tools are located. |
|
scope |
sample|project |
Where the ‘bdg’ is located |
Note
Set script_path to the path of the UCSC tools, not to a specific tool!!! If they are in the PATH, as when installing with CONDA, leave the script_path empty.
Both bedGraphToBigWig and bigWigToWig will be executed. To set specific params, use bedGraphToBigWig_params and bigWigToWig_params, respectively.
Lines for parameter file
UCSCmap_bams:
module: UCSC_BW_wig
base: genCovBed_sam
script_path: /path/to/ucscTools/kentUtils/bin/
genome: /path/to/ref_genome.chrom.sizes
bedGraphToBigWig_params: -blockSize=10 -itemsPerSlot=20
bigWigToWig_params: -chrom X1 -start X2 -end X3
References
Kent, W.J., Zweig, A.S., Barber, G., Hinrichs, A.S. and Karolchik, D., 2010. BigWig and BigBed: enabling browsing of large distributed datasets. Bioinformatics, 26(17), pp.2204-2207.
IGV_count *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running IGVtools count:
Requires
Either SAM or BAM files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
Output
Puts output tdf or wig files in one the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["wig"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["tdf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
format |
wig|tdf |
Determines whether to create a ‘wig’ or ‘tdf’ file. |
genome |
Path to chrom.sizes file for reference genome |
Lines for parameter file
IGVcount1:
module: IGV_count
base: samtools1
script_path: java -Xmx1500m -jar /path/to/igvtools.jar count
format: tdf # Options: 'tdf' or 'wig'
genome: /path/to/genome.chrom.sizes
References
Thorvaldsdóttir, H., Robinson, J.T. and Mesirov, J.P., 2013. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Briefings in bioinformatics, 14(2), pp.178-192.
IGV_toTDF *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running IGVtools toIGV:
Requires
WIG file in the following slot:
sample_data[<sample>]["wig"]
Output
Puts output tdf file in one the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["tdf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome |
Path to chrom.sizes file for reference genome |
Lines for parameter file
IGV2TDF:
module: IGV_toTDF
base: samtools1
script_path: /path/to/bin/java -Xmx1500m -jar /path/to/igvtools.jar toTDF
genome: /path/to/genome.chrom.sizes
References
Thorvaldsdóttir, H., Robinson, J.T. and Mesirov, J.P., 2013. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Briefings in bioinformatics, 14(2), pp.178-192.
ChIP-seq
Modules included in this section
macs2_callpeak *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running macs2 callpeak:
Requires
bam files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]
If using control (input) samples, make sure you include a sample-control table in your sample file.
Output
Puts output macs2 output files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["prefix"])self.sample_data[<sample>]["peak_bed"])self.sample_data[<sample>]["peak_xls"])self.sample_data[<sample>]["summit_bed"])
If
--bdg(or-B) was specified, puts output bdg files in the following slots:self.sample_data[<sample>]["control_lambda"]- Control BedGraphself.sample_data[<sample>]["treat_pileup"]- Treatment BedGraphself.sample_data[<sample>]["bdg"]- Treatment BedGraphself.sample_data[<control>]["bdg"]- Control BedGraph
If
bedToBigBed_pathwas specified, puts output bigbed files in the following slots:self.sample_data[<sample>]["bb"]
If
getfastawas specified, puts output fasta files in the following slots:self.sample_data[<sample>]["peak_fasta"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
bedToBigBed_path |
path to bedToBigBed |
Runs bedToBigBed to convert the peak bed files into bigbed for uploading to UCSC. |
chrom.sizes |
path to chrom.sizes for reference genome |
If running bedToBigBed, you must supply the genome chrom.sizes file. |
getfasta |
If set, a fasta file containing the peak sequences will be produced. |
Lines for parameter file
macs1_CP:
module: macs2_callpeak
base: samtools1
script_path: /path/to/bin/macs2 callpeak
bedToBigBed_path: /path/to/kentUtils/bin/bedToBigBed
chrom.sizes: /path/to/genome.chrom.sizes
getfasta: /path/to/bedtools getfasta -name -s
redirects:
--SPMR:
--bdg:
-g: mm
--bw: 400
References
Feng, J., Liu, T., Qin, B., Zhang, Y. and Liu, X.S., 2012. Identifying ChIP-seq enrichment using MACS. Nature protocols, 7(9), pp.1728-1740.
macs2_bdgcmp
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running macs2 bdgcmp:
Requires
Files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["control_lambda"]- Control BedGraphself.sample_data[<sample>]["treat_pileup"]- Treatment BedGraph
Output
Puts output macs2 output files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["bdg"])- The comparison bedgraph!self.sample_data[<sample>]["bigwig"])- ifslop_pathanducscTools_pathwere passedself.sample_data[<sample>]["wig"])- ifslop_pathanducscTools_pathwere passedself.sample_data[<sample>]["tdf"])- in TDF format (ifslop_path,ucscTools_pathandtoTDF_pathwere passed)
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
slop_path |
path to bedtools slop |
Is part of the process for converting bdg files into bigwig and wig |
ucscTools_path |
path to ucscTools |
UCSCtools bedClip, bedGraphToBigWig and bigWigToWig are part of the process for converting bdg files into bigwig and wig |
toTDF_path |
path to toTDF |
Converts the wig file into TDF file. |
genome |
path to chrom.sizes for reference genome |
If running bedToBigBed, you must supply the genome chrom.sizes file. |
Lines for parameter file
bdgcmp:
module: macs2_bdgcmp
base: macs1
script_path: /path/to/macs2 bdgcmp
genome: /path/to/chrom.sizes.txt
slop_path: /path/to/bin/bedtools slop
ucscTools_path: /path/to/ucscTools/bin
toTDF_path: /path/to/bin/java -Xmx1500m -jar /path/to/igvtools.jar toTDF
redirects:
--method: FE
References
Feng, J., Liu, T., Qin, B., Zhang, Y. and Liu, X.S., 2012. Identifying ChIP-seq enrichment using MACS. Nature protocols, 7(9), pp.1728-1740.
CEAS
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running CEAS:
Requires
Files in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["peak_bed"]- Samplepeak_bedfileself.sample_data[<sample>]["wig"]- An appropriatewigfile
Output
Puts CEAS output files in the following slots:
sample_data[sample]["CEAS.xls"]sample_data[sample]["CEAS.R"]sample_data[sample]["CEAS.plots"]
Parameters that can be set
Lines for parameter file
CEAS1:
module: CEAS
base: UCSC_BW_to_wig
script_path: /path/to/bin/ceas
redirects:
-g: /path/to/hg19.refGene
References
Shin, H., Liu, T., Manrai, A.K. and Liu, X.S., 2009. CEAS: cis-regulatory element annotation system. Bioinformatics, 25(19), pp.2605-2606.
Genome Assembly
Modules included in this section
clc_assembl
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for assembling reads using CLC assembler.
Requires
fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output:
puts fasta output files in the following slots:
if
scopeset tosample:sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["clc_assembl.contigs"]Also, sets
sample_data[<sample>]["assembler"] = "clc_assembl"
if
scopeset toproject:sample_data["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["clc_assembl.contigs"]Also, sets
sample_data[<sample>]["assembler"] = "clc_assembl"
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
Set to |
p |
e.g. ‘fb ss 180 250’ |
Sets the |
Lines for parameter file
clc1:
module: clc_assembl
base: trim1
script_path: /path/to/clc_assembler
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 30
node: sge37
scope: sample
p: fb ss 180 250
redirects:
--cpus: 30
megahit_assembl
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for assembling reads using MEGAHIT assembler.
Requires
fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output:
puts fasta output files in the following slots:
if
scopeset tosample:sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["megahit_assembl.contigs"]Also, sets
sample_data[<sample>]["assembler"] = "megahit_assembl"
if
scopeset toproject:sample_data["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["megahit_assembl.contigs"]Also, sets
sample_data[<sample>]["assembler"] = "megahit_assembl"
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
Set to |
Lines for parameter file
megahit1:
module: megahit_assembl
base: trim1
script_path: /path/to/megahit
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 30
node: sge37
scope: project
redirects:
--continue:
--num-cpu-threads: 30
References
Li, D., Liu, C.M., Luo, R., Sadakane, K. and Lam, T.W., 2015. MEGAHIT: an ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics, 31(10), pp.1674-1676.
spades_assembl *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for assembling reads using spades assembler.
Requires
fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output:
puts fasta output files in the following slots:
for sample-wise assembly:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
sample_data[<sample>]["spades_assembl.contigs"]
sample_data[<sample>]["spades_assembl.scaffolds"]for mega assembly (not defined yet):
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
sample_data["spades_assembl.contigs"]
sample_data["spades_assembl.scaffolds"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
Set if project-wide fasta slot should be used |
truncate_names |
truncates contig names, e.g. ‘>NODE_82_length_18610_cov_38.4999_ID_165’ will be changed to ‘>NODE_82_length_18610’ |
|
use_corrected |
Use the reads files after reads correction for douwnstream usge |
Lines for parameter file
spades1:
module: spades_assembl
base: trim1
script_path: /path/to/bin/spades.py
truncate_names:
redirects:
--careful:
References
Bankevich, A., Nurk, S., Antipov, D., Gurevich, A.A., Dvorkin, M., Kulikov, A.S., Lesin, V.M., Nikolenko, S.I., Pham, S., Prjibelski, A.D. and Pyshkin, A.V., 2012. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. Journal of computational biology, 19(5), pp.455-477.
quast *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running quast on fasta assemblies:
QUAST is executed on the fasta file along the following lines:
If ‘scope’ is specified, the appropriate fasta will be used. An error will occur if the fasta does not exist.
If ‘scope’ is not specified, if a project-wide fasta exists, it will be used. Otherwise, sample-wise fasta files will be used. If none exist, an error will occur.
Note
With compare_mode, you tell the module to run quast on multiple assemblies. This is done in one of three ways:
If
scopeis sample and a single base step defined, will compare between the samples.If
scopeis sample and there is more than one base step defined, will compare between the assemblies found in the base steps for each sample separately.If
scopeis project, will compare between the assemblies found in the base steps at the project level.
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
Output
- Puts output directory in one of:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["quast"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["quast"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project or sample contigs file. |
compare_mode |
If ‘scope’ is ‘sample’, specifies whether to analyse each sample separately or to create a single comparison report for all samples. |
Lines for parameter file
A quast report for each sample separately:
quast1:
module: quast
base: spades1
script_path: /path/to/quast.py
scope: sample
redirects:
--fast:
A quast report comparing the sample assemblies:
quast1:
module: quast
base: spades1
script_path: /path/to/quast.py
compare_mode:
scope: sample
redirects:
--fast:
A quast report comparing the project assemblies from different stages of the analysis:
quast1:
module: quast
base:
- spades1
- megahit1
script_path: /path/to/quast.py
compare_mode:
scope: project
redirects:
--fast:
References
Gurevich, A., Saveliev, V., Vyahhi, N. and Tesler, G., 2013. QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 29(8), pp.1072-1075.
Transcriptome Assembly
Modules included in this section
trinity *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for RNA_seq assembly using the Trinity assembler.
Attention
This module was tested on release 2.5.x. It should also work with 2.4.x
For old versions of Trinity, you might need to use trinity_old module.
The main difference between the modules is that trinity creates an output directory with the word trinity in it as required by the newer release of Trinity.
In order to run on the cluster, you need to install HpcGridRunner.
Requires
fastqfiles in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
bamfile for Genome Guided assembly in:sample_data["bam"]sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]
Output:
puts
fastaoutput files in the following slots:
for sample-wise assembly:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
sample_data[<sample>]["Trinity.contigs"]for project-wise assembly:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
sample_data["Trinity.contigs"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
Set if project-wide fasta slot should be used |
skip_gene_to_trans_map |
Set to skip construction of the transcript map. You can use a dedicated module, |
|
get_Trinity_gene_to_trans_map |
Path to get_Trinity_gene_to_trans_map.pl. If not passed, will try guessing from Trinity path |
|
TrinityStats |
block with ‘path:’ set to TrinityStats.pl executable |
|
genome_guided |
Use if you have a project level BAM file with reads mapped to a reference genome and it is coordinate sorted |
|
Group_by |
Name of the Column in the grouping file to use for grouping |
Only works in project scope: Will create a sample file for Trinity |
Lines for parameter file
trinity1:
module: trinity
base: trin_tags1
script_path: {Vars.paths.Trinity}
qsub_params:
node: sge213
-pe: shared 20
redirects:
--grid_exec: "{Vars.paths.hpc_cmds_GridRunner} --grid_conf {Vars.paths.SGE_Trinity_conf} -c"
--grid_node_CPU: 40
--grid_node_max_memory: 80G
--max_memory: 80G
--seqType: fq
--min_kmer_cov: 2
--full_cleanup:
TrinityStats:
path: {Vars.paths.TrinityStats}
References
Grabherr, M.G., Haas, B.J., Yassour, M., Levin, J.Z., Thompson, D.A., Amit, I., Adiconis, X., Fan, L., Raychowdhury, R., Zeng, Q. and Chen, Z., 2011. Trinity: reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nature biotechnology, 29(7), p.644.
Trinity_gene_to_trans_map
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for creating a gene vs. transcript map for a Trinity based assembly.
Requires
fastafiles in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"](ifscope = sample)
sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"](ifscope = project)
Output:
puts gene to trans map in:
sample_data[<sample>]["gene_trans_map"](ifscope = sample)
sample_data["project_data"]["gene_trans_map"](ifscope = project)
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
Use sample or project scope assembly. |
Lines for parameter file
Gene_Trans_Map:
module: Trinity_gene_to_trans_map
base: trinity
script_path: {Vars.paths.get_Trinity_gene_to_trans_map.pl}
References
Grabherr, M.G., Haas, B.J., Yassour, M., Levin, J.Z., Thompson, D.A., Amit, I., Adiconis, X., Fan, L., Raychowdhury, R., Zeng, Q. and Chen, Z., 2011. Trinity: reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nature biotechnology, 29(7), p.644.
trinity_mapping
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for running align_and_estimate_abundance.pl on a Trinity assembly and the raw reads.
Tested on versions 2.4.0 and 2.5.0 of Trinity.
See the align_and_estimate_abundance.pl script documentation.
Requires
fastqfiles in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]A Trinity assembly in one of (depending on
scope)
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output:
Puts output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]sample_data[<sample>]["unsorted_bam"](If--coordsort_bamis passed in redirects)sample_data[<sample>]["isoforms.results"]sample_data[<sample>]["genes.results"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
Set if project-wide fasta slot should be used |
redirects: –gene_trans_map |
path or empty |
If empty, use internal gene_trans_map. If path, use path as gene_trans_map for all samples. If not passed, performs analysis on isoform level only |
redirects: –trinity_mode |
If set, will create a gene_trans_map for each sample and store it as sample gene_trans_map |
Lines for parameter file
trin_map1:
module: trinity_mapping
base: trinity1
script_path: {Vars.paths.align_and_estimate_abundance}
redirects:
--est_method: RSEM
--aln_method: bowtie
--trinity_mode:
--seqType: fq
References
Grabherr, M.G., Haas, B.J., Yassour, M., Levin, J.Z., Thompson, D.A., Amit, I., Adiconis, X., Fan, L., Raychowdhury, R., Zeng, Q. and Chen, Z., 2011. Trinity: reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nature biotechnology, 29(7), p.644.
trinity_statistics
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for running abundance_estimates_to_matrix.pl on genes or isoforms counts tables produced by align_and_estimate_abundance.pl
See the script documentation here.
This conversion makes sense at the project level - combining all sample matrices into a single, normalized, comparison table. However, for completeness, we included a sample scope option for running the script in each sample separately.
Note
scope is not defined for this module. It only makes sense to run abundance_estimates_to_matrix when comparing many samples against a single assembly
Requires
Either
genes.resultsorisoforms.resultsfiles in the following slots:sample_data[<sample>]["genes.results"]sample_data[<sample>]["isoforms.results"]
Output:
Creates the following files in the following slots:
<project>.counts.matrixinself.sample_data["project_data"]["counts.matrix"]<project>.not_cross_norm.fpkm.tmpinself.sample_data["project_data"]["not_cross_norm.fpkm.tmp"]<project>.not_cross_norm.fpkm.tmp.TMM_info.txtinself.sample_data["project_data"]["not_cross_norm.fpkm.tmp.TMM_info.txt"]<project>.TMM.fpkm.matrixinself.sample_data["project_data"]["TMM.fpkm.matrix"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
use_genes |
Use ‘genes.results’ matrix. If not passed, use ‘isoforms.results’ |
|
redirects: –gene_trans_map |
path or ‘none’ |
If path, use path as gene_trans_map for all samples. If ‘none’, does not produce gene level estimates. In order to use an internal gene_trans_map, do not pass this parameter! |
Lines for parameter file
trin_map_stats:
module: trinity_statistics
base: trin_map1
script_path: /path/to/abundance_estimates_to_matrix.pl
use_genes:
redirects:
--est_method: RSEM
References
Grabherr, M.G., Haas, B.J., Yassour, M., Levin, J.Z., Thompson, D.A., Amit, I., Adiconis, X., Fan, L., Raychowdhury, R., Zeng, Q. and Chen, Z., 2011. Trinity: reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nature biotechnology, 29(7), p.644.
RSEM
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Short Description
A module for running RSEM
Requires
- fastq file in
self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.F"]self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.R"]self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.S"]
- or bam file in
self.sample_data[sample]["bam"]
Output
- puts output bam files (if the input is fastq) in:
self.sample_data[sample]["bam"]
- puts the location of RSEM results in:
self.sample_data[sample]["RSEM"]self.sample_data[sample]["genes.results"]self.sample_data[sample]["isoforms.results"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
mode |
transcriptome/genome |
Is the reference is a genome or a transcriptome? |
gff3 |
None |
Use if the mode is genome and the annotation file is in gff3 format |
Comments
- This module was tested on:
RSEM v1.2.25bowtie2 v2.2.6
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: RSEM # Name of the module used
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a bam file generator step or merge with fastq files]
script_path: # Command for running the RSEM script
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
mode: # transcriptome or genome
export_transcriptome: # In genome mode set the extracted transcriptome as the new project level fasta.nucl and extract the ranscript-to-gene-map file as project level gene_trans_map
annotation: # For Genome mode: the location of GTF file [the default] , for GFF3 use the gff3 flag. For Transcriptome mode: transcript-to-gene-map file.
# If annotation is set to Trinity the transcript-to-gene-map file will be generated using the from_Trinity_to_gene_map script
# If not set will use only the reference file as unrelated transcripts
from_Trinity_to_gene_map_script_path: # If the mode is transcriptome and the reference was assembled using Trinity it is possible to generate the transcript-to-gene-map file automatically using this script
# If annotation is set to Trinity and this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
gff3: # Use if the mode is genome and the annotation file is in gff3 format
mapper: # bowtie/bowtie2/star
mapper_path: # Location of mapper script
rsem_prepare_reference_script_path: # Location of preparing reference script
plot_stat: # Generate statistical plots
plot_stat_script_path: # Location of statistical plot generating script
reference: # The reference genome/transcriptome location [FASTA file]
rsem_generate_data_matrix_script_path: # Location of the final matrix generating script
# If this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
redirects:
--append-names: # RSEM will append gene_name/transcript_name to the result files
--estimate-rspd: # Enables RSEM to learn from the data how the reads are distributed across a transcript
-p: # Number of CPUs to use in this analysis
--bam: # Will use bam files and not fastq
--no-bam-output:
--output-genome-bam: # Alignments in genomic coordinates (only if mode is genome)
References
Li, Bo, and Colin N. Dewey. “RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome.” BMC bioinformatics 12.1 (2011): 323.
quast *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running quast on fasta assemblies:
QUAST is executed on the fasta file along the following lines:
If ‘scope’ is specified, the appropriate fasta will be used. An error will occur if the fasta does not exist.
If ‘scope’ is not specified, if a project-wide fasta exists, it will be used. Otherwise, sample-wise fasta files will be used. If none exist, an error will occur.
Note
With compare_mode, you tell the module to run quast on multiple assemblies. This is done in one of three ways:
If
scopeis sample and a single base step defined, will compare between the samples.If
scopeis sample and there is more than one base step defined, will compare between the assemblies found in the base steps for each sample separately.If
scopeis project, will compare between the assemblies found in the base steps at the project level.
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
Output
- Puts output directory in one of:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["quast"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["quast"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project or sample contigs file. |
compare_mode |
If ‘scope’ is ‘sample’, specifies whether to analyse each sample separately or to create a single comparison report for all samples. |
Lines for parameter file
A quast report for each sample separately:
quast1:
module: quast
base: spades1
script_path: /path/to/quast.py
scope: sample
redirects:
--fast:
A quast report comparing the sample assemblies:
quast1:
module: quast
base: spades1
script_path: /path/to/quast.py
compare_mode:
scope: sample
redirects:
--fast:
A quast report comparing the project assemblies from different stages of the analysis:
quast1:
module: quast
base:
- spades1
- megahit1
script_path: /path/to/quast.py
compare_mode:
scope: project
redirects:
--fast:
References
Gurevich, A., Saveliev, V., Vyahhi, N. and Tesler, G., 2013. QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 29(8), pp.1072-1075.
htseq_count
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running htseq-count:
See htseq-count documentation.
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
Output
- Puts the output file in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["HTSeq.counts"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
gff |
path to bowtie1 index |
If not given, will look for a project bowtie1 index and then for a sample bowtie1 index |
-f|–format |
sam | bam |
In redirects. Tells htseq-count which file to use. If not specified, will use whichever file exists. |
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
htseq_c1:
module: htseq_count
base: samtools_STAR1
script_path: /storage16/app/bioinfo/python_packages/bin/htseq-count
gtf: /fastspace/bioinfo_databases/STAR_GRCh38_Gencode21/gencode.v21.annotation.gtf
redirects:
--format: bam
-s: 'no'
-m: intersection-nonempty
References
Anders, S., Pyl, P.T. and Huber, W., 2015. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics, 31(2), pp.166-169.
Transcriptome Annotation
Modules included in this section
Trinotate
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for RNA_seq assembly annotation using Trinotate.
Note
This module will be updated in the future to support uploading of other sources of information such as RNAMMER output. See Trinotate documentation.
Requires
- A transcripts file in
self.sample_data[“project_data”][“transcripts.fasta.nucl”],
- A gene to transcript mapping file in: (produced by
Trinity_gene_to_trans_mapmodule) self.sample_data[“project_data”][“gene_trans_map”],
- A gene to transcript mapping file in: (produced by
- A protein fasta file (produced by
TransDecoder) self.sample_data[“project_data”][“fasta.prot”])
- A protein fasta file (produced by
- Results of
blastpof protein file against swissprot database: self.sample_data[“project_data”][“blast.prot”],
- Results of
- Results of
blastxof transcripts file against swissprot database: self.sample_data[“project_data”][“blast.nucl”],
- Results of
- Results of
hmmscanof protein file against pfam database: self.sample_data[“project_data”][“hmmscan.prot”])
- Results of
- Results of
signalpof protein file using signalp program: [ optional ] self.sample_data[“project_data”][“signalp”])
- Results of
- Results of
rnammer/infernaltranscripts of file: [ optional, use Infernal with Trinotate-V4 ] self.sample_data[“project_data”][“rnammer”])
- Results of
- Results of
tmhmmof protein file using TmHMM program: [ optional ] self.sample_data[“project_data”][“tmhmm”])
- Results of
- Results of
eggnogof protein file using EggnogMapper program: [ optional only Trinotate-V4] self.sample_data[“project_data”][“eggnog”])
- Results of
Attention
If scope is set to sample, all of the above files should be in the sample scope!
Output:
puts Trinotate report file in:
sample_data[<sample>]["trino.rep"](scope = sample)sample_data["trino.rep"](scope = project)
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
|
sqlitedb |
Path to Trinotate sqlitedb |
|
cp_sqlitedb |
Create local copy of the sqlitedb, before loading teh data (recommended) |
|
ver4 |
Indicate you are using Trinotate V4 |
Lines for parameter file
trino_Trinotate:
module: Trinotate
base:
- trino_blastp_sprot
- trino_blastx_sprot
- trino_hmmscan1
script_path: {Vars.paths.Trinotate}
scope: project
sqlitedb: {Vars.databases.trinotate.sqlitedb}
cp_sqlitedb:
ver4:
References
Grabherr, M.G., Haas, B.J., Yassour, M., Levin, J.Z., Thompson, D.A., Amit, I., Adiconis, X., Fan, L., Raychowdhury, R., Zeng, Q. and Chen, Z., 2011. Trinity: reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nature biotechnology, 29(7), p.644.
TransDecoder
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running TransDecoder on a transcripts file.
Note
Tested on TransDecoder version 5.5.0.. The main difference being that in this version an output directory can be specified in the command line.
Requires
fasta files in at least one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"](ifscope = sample)
sample_data["fasta.nucl"](ifscope = project)
Output:
If
scope = project:Protein fasta in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.prot"]Gene fasta in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]Original transcripts in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["transcripts.fasta.nucl"]GFF file in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["gff3"]
If
scope = sample:Protein fasta in
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.prot"]Gene fasta in
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]Original transcripts in
self.sample_data[<sample>]["transcripts.fasta.nucl"]GFF file in
self.sample_data[<sample>]["gff3"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample|project |
Determine weather to use sample or project transcripts file. |
Lines for parameter file
trino_Transdecode_highExpr:
module: TransDecoder
base: Split_Fasta
script_path: {Vars.paths.TransDecoder}
scope: sample
References
RNASeq
Modules included in this section
DeSeq2
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Short Description
A module to preform: * Gene level differential expression using DeSeq2. * Gene annotation. * PCA plot. * Clustering of significant genes. * Heatmaps of significant genes by clusters. * Expression patterns plot by clusters * Enrichment analysis KEGG/GO.
Requires
- Search for count data in :
self.sample_data[<sample>][“RSEM”] self.sample_data[<sample>][“genes.counts”] self.sample_data[<sample>][“HTSeq.counts”] self.sample_data[“project_data”][“results”]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
use_click |
Will use the CLICK clustering program (Shamir et al. 2000) |
Note
If your using the use_click option, cite: Expander: Ulitsky I, Maron-Katz A, Shavit S, Sagir D, Linhart C, Elkon R, Tanay A, Sharan R, Shiloh Y, Shamir R. Expander: from expression microarrays to networks and functions. Nature Protocols Vol 5, pp 303 - 322, 2010 Click: Shamir , R. and Sharan, R. CLICK: A Clustering Algorithm with Applications to Gene Expression Analysis. Proceedings ISMB 2000, pp.307-316 (2000)
Comments
- The following R packages are required:
DESeq2ggplot2pheatmapmclustfactoextracowplotgridExtrabiomaRtclusterProfilerKEGGRESTscatersvarmarkdownplotlydtxml2dplyrrcolorbrewercolorspacestringr
Note
It is Possible to use CONDA to install all dependencies:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bioinfo-core-BGU/neatseq-flow-modules/master/neatseq_flow_modules/Liron/DeSeq2_module/DeSeq2_env_install.yaml
conda env create -f DeSeq2_env_install.yaml
Flow this Tutorial for More Information.
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: DeSeq2 # Name of the used module
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after with count results.
script_path: # Command for running the a DeSeq2 script
# If this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
use_click: # Will use the CLICK clustering program (Shamir et al. 2000).
redirects:
--SAMPLE_DATA_FILE: # Path to Samples Information File
--GENE_ID_TYPE: # The Gene ID Type i.e 'ENSEMBL'[for Bioconductor] OR 'ensembl_gene_id'/'ensembl_transcript_id' [for ENSEMBL]
--Annotation_db: # Bioconductor Annotation Data Base Name from https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/BiocViews.html#___OrgDb
--Species: # Species Name to Retrieve Annotation Data from ENSEMBL
--KEGG_Species: # Species Name to Retrieve Annotation Data from KEGG
--KEGG_KAAS: # Gene to KO file from KEGG KAAS [first column gene id, second column KO number]
--Trinotate: # Path to a Trinotate annotation file in which the first column is the genes names
--FILTER_SAMPLES: # Filter Samples with Low Number of expressed genes OR with Small Library size using 'scater' package
--FILTER_GENES: # Filter Low-Abundance Genes using 'scater' package
--NORMALIZATION_TYPE: # The DeSeq2 Normalization Type To Use [VSD , RLOG] The Default is VSD
--BLIND_NORM: # Perform Blind Normalization
--DESIGN: # The Main DeSeq2 Design [ ~ Group ]
--removeBatchEffect # Will Remove Batch Effect from the Normalized counts data up to 2
# [using the limma package and only one using the sva package]
# Batch Effect fields [from the Sample Data ] separated by ,
--removeBatchEffect_method # The method to Remove Batch Effect from the Normalized counts data using the limma or sva packages [sva is the default]
--LRT: # The LRT DeSeq2 Design
--ALPHA: # Significant Level Cutoff, The Default is 0.05
--Post_statistical_ALPHA # Post Statistical P-value Filtering
--FoldChange: # Fold change Cutoff [testing for fold changes greater in absolute value], The Default is 1
--Post_statistical_FoldChange # Post Statistical Fold change Filtering
--CONTRAST: # The DeSeq Contrast Design ["Group,Treatment,Control"] [Not For LTR] .
# It is possible to define more then one contrast Design ["Group,Treatment1,Control1|Group,Treatment2,Control2|..."]
--SPLIT_BY_CONTRAST # Only use Samples found in the relevant contrast for Clustering and Enrichment Analysis
--modelMatrixType: # How the DeSeq model matrix of the GLM formula is formed [standard or expanded] ,The Default is standard
--GENES_PLOT: # Genes Id To Plot count Data [separated by ',']
--X_AXIS: # The Filed In the Sample Data To Use as X Axis
--GROUP: # The Filed In the Sample Data To Group By [can be two fields separated by ',']
--SPLIT_BY: # The Filed In the Sample Data To Split the Analysis By.
--FUNcluster: # A clustering function including [kmeans,pam,clara,fanny,hclust,agnes,diana,click]. The default is hclust
# If the 'use_click' option is used the '--FUNcluster' option is set to 'click'
--hc_metric: # Hierarchical clustering metric to be used for calculating dissimilarities between observations. The default is pearson
--hc_method: # Hierarchical clustering agglomeration method to be used. The default is ward.D2
--k.max: # The maximum number of clusters to consider, must be at least two. The default is 20
--nboot: # Number of Monte Carlo (bootstrap) samples for determining the number of clusters [Not For Mclust]. The default is 10
--stand: # The Data will be Standardized Before Clustering.
--Mclust: # Use Mclust for determining the number of clusters.
--CLICK_HOMOGENEITY: # The HOMOGENEITY [0-1] of clusters using CLICK program (Shamir et al. 2000). The default is 0.5
--PCA_COLOR: # The Filed In the Sample Data To Determine Color In The PCA Plot
--PCA_SHAPE: # The Filed In the Sample Data To Determine Shape In The PCA Plot
--PCA_SIZE: # The Filed In the Sample Data To Determine Size In The PCA Plot. The default is Library Size
--Enriched_terms_overlap: # Test for genes overlap in enriched terms
--USE_INPUT_GENES_AS_BACKGROUND # Use The input Genes as the Background for Enrichment Analysis
--only_clustering # Don't Perform Differential Analysis!!!
--significant_genes # Use these genes as the set of significant genes [a comma separated list]
--collapseReplicates # Will collapse technical replicates using a Sample Data field indicating which samples are technical replicates
Sequence Annotation
Modules included in this section
Prokka
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
Short Description
Runs Prokka on all samples
Requires
- For each Sample, a fasta.nucl file type [e.g. an assembly result] in:
sample_data[sample]["fasta.nucl"]
Output
- For each Sample, puts the location of the Sample’s GFF file in:
sample_data[sample]["GFF"]
- For each Sample, puts the location of the Sample’s identified genes file in:
sample_data[sample]["fasta.nucl"]
- For each Sample, puts the location of the Sample’s identified genes [translated] file in:
sample_data[sample]["fasta.prot"]
- if generate_GFF_dir option exist, puts the directory location of all Samples GFFs in:
sample_data["GFF_dir"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
generate_GFF_dir |
Create GFF directory |
Comments
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Prokka # Name of the module to use
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a fasta file generator step like an assembly program or start the analysis with fasta files]
script_path: # Command for running Prokka
env: # env parameters that needs to be in the PATH for running this module
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
generate_GFF_dir: # Create GFF directory
redirects:
--cpus: # parameters for running Prokka
--force: # parameters for running Prokka
--genus: # parameters for running Prokka
--kingdom: # parameters for running Prokka
--proteins: # Use the location of a protein DB [FASTA] for extra annotation or use "VFDB" to use the module VFDB built-in virulence/resistance DB
References
Seemann, Torsten. “Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation.” Bioinformatics 30.14 (2014): 2068-2069.
prokka_old *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running prokka:
Prokka is executed on the contigs stored in sample_data.
Requires
A nucleotide fasta file in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
If
scopeis set tosample:- Puts output predicted protein sequences (faa file) in:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.prot"]
- Puts output predicted protein genomic sequences (fna file) in:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
- Puts the annotation file (gff) in:
sample_data[<sample>]["gff"]
- Stores the prokks dir in:
sample_data[<sample>]["prokka.dir"]
If
scopeis set toproject:- Puts output predicted protein sequences (faa file) in:
sample_data["fasta.prot"]
- Puts output predicted protein genomic sequences (fna file) in:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
- Puts the annotation file (gff) in:
sample_data["gff"]
- Stores the prokks dir in:
sample_data["prokka.dir"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
generate_GFF_dir |
empty |
Create a dir with links to the gff files for use downstream by others. Only relevant when |
Comments
If you set values to --locustag, --genus, --species and --strain, these will hold for all the samples, and will be passed as-is to the scripts.
If you pass the parameters without setting their values, the values will be set to the sample names (or to the project name, when scope == 'project').
Lines for parameter file
prokka1:
module: prokka_old
base: spades1
script_path: /path/to/prokka
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
generate_GFF_dir:
scope: sample
redirects:
--cpus: 20
--fast:
--force:
--genus: Staphylococcus
--metagenome:
--strain:
References
Seemann, T., 2014. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics, 30(14), pp.2068-2069.
Metagenomics
Modules included in this section
HUMAnN2
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running HUMAnN2:
Requires
fastq files, either forward or single:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
Puts the
HUMAnN2output files in:self.sample_data[sample]["HUMAnN2.genefamilies"](Also inHUMAnN2.genefamilies.RPK)self.sample_data[sample]["HUMAnN2.pathabundance"](Also inHUMAnN2.pathabundance.RPK)self.sample_data[sample]["HUMAnN2.pathcoverage"]
If
humann2_renorm_tableblock is set in params, puts the normalized tables in:self.sample_data[sample]["HUMAnN2.genefamilies"](Also inHUMAnN2.genefamilies.<units>, where<units>is the value passed to--units)self.sample_data[sample]["HUMAnN2.pathabundance"](Also inHUMAnN2.pathabundance.<units>, where<units>is the value passed to--units)
If
humann2_join_tablesblock is set in params, puts the joined tables in:self.sample_data["project_data"]["HUMAnN2.genefamilies"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["HUMAnN2.pathabundance"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["HUMAnN2.pathcoverage"]
Note
If both humann2_renorm_table and humann2_join_tables blocks exist in params, humann2_join_tables will work on the normalized tables produced by humann2_renorm_table! To join the non-normalized tables, do not normalize the tables by not including a humann2_renorm_table block.
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
humann2_join_tables |
Block containing |
|
humann2_renorm_table |
Block containing |
|
protein-database |
uniref50|uniref90 |
Protein database used for analysis. |
Warning
The protein-database parameter records the protein database being used: uniref50 or uniref90. It is not used by this module but is required by the downstream module, HUMAnN2_further_processing. If you do not include it, you will not be able to add a HUMAnN2_further_processing instance for downstream analysis.
Lines for parameter file
HUMAnN2_uniref50_hardtrimmed_reads:
module: HUMAnN2
base: Trim_Galore
script_path: '{Vars.Programs_path.humann2}'
setenv: PERL5LIB="" mpa_dir=$CONDA_PREFIX/bin
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 30
protein-database: uniref50
redirects:
--gap-fill: 'on'
--input-format: fastq
--minpath: 'on'
--nucleotide-database: '{Vars.databases.humann2.chocophlan}'
--protein-database: '{Vars.databases.humann2.uniref50}'
--threads: '30'
humann2_join_tables:
path: humann2_join_tables
humann2_renorm_table:
path: humann2_renorm_table
redirects:
--units: cpm
References
kraken
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running kraken:
Note that kraken executable must be in a folder together with kraken-translate and kraken-report. This is the default for kraken installation.
Pass the full path to the kraken executable in script_path.
Merging of sample kraken reports in done with krona. See the section on Parameters that can be set.
You can follow this module with the kraken-biom module to create a biom table from the reports.
Requires
fastq files, either paired end or single:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
Puts the
krakenoutput files in:self.sample_data[<sample>]["raw_classification"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["classification"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["kraken.report"]If
ktImportTaxonomy_pathparameter was passed, puts the krona reports inself.sample_data["project_data"]["krona"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
ktImportTaxonomy_path |
Path to ktImportTaxonomy. You can additional |
Lines for parameter file
kraken1:
module: kraken
base: trim1
script_path: {Vars.paths.kraken}
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
ktImportTaxonomy_path: /path/to/ktImportTaxonomy -u http://krona.sourceforge.net
redirects:
--db: /path/to/kraken_std_db
--preload:
--quick:
--threads: 20
References
Wood, D.E. and Salzberg, S.L., 2014. Kraken: ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genome biology, 15(3), p.R46.
kraken_biom
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running kraken-biom (https://github.com/smdabdoub/kraken-biom)
Requires
Kraken reports:
sample_data[<sample>]["kraken.report"]
Output
Puts the resulting biom output files in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["kraken.biom"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_tsv"](ifskip_tsvis not set)
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
skip_tsv |
Set if you do not want to convert the report into tsv format. |
|
skip_summary |
Set if you do not want to create a summary of the report. |
|
biom_path |
/path/to/biom |
The path to biom. This is required for conversion to tsv and for producing the summary |
Lines for parameter file
kraken_biom1:
module: kraken_biom
base: kraken1
script_path: '{Vars.paths.kraken_biom}'
# skip_tsv:
biom_path: '{Vars.paths.biom}'
redirects:
--max: D
--min: S
--gzip:
References
metaphlan2
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running metaphlan2:
Requires
fastq files, either paired end or single:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
Puts the
metaphlan2output files in:self.sample_data[<sample>]["raw_classification"]
If
If
ktImportText_pathparameter was passed, puts the krona reports inself.sample_data["project_data"]["krona"]
If
merge_metaphlan_tableswas passed, puts the merged reports inself.sample_data["project_data"]["merged_metaphlan2"]
If ‘–biom’ is set in
redirects, the biom table is put in:self.sample_data[<sample>]["biom_table"]
If ‘–bowtie2out’ is set in
redirects, the SAM file is put in:self.sample_data[<sample>]["sam"]
If ‘metaphlan2krona_path’ is set:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["classification"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
ktImportText_path |
Path to ktImportText. |
|
merge_metaphlan_tables |
Path to merge_metaphlan_tables.py. If not specified, will derive it from the location of |
|
metaphlan2krona_path |
Path to metaphlan2krona.py |
Lines for parameter file
metph1:
module: metaphlan2
base: trim1
script_path: {Vars.paths.metaphlan2}
ktImportText_path: /path/to/ktImportText
merge_metaphlan_tables:
metaphlan2krona_path: /path/to/metaphlan2krona.py
redirects:
--biom:
--bowtie2_exe: /path/to/bowtie2
--bowtie2db: /path/to/database
--bowtie2out:
--input_type: fastq
--mdelim: ';'
--mpa_pkl: /path/to/mpa_v20_m200.pkl
References
Truong, D.T., Franzosa, E.A., Tickle, T.L., Scholz, M., Weingart, G., Pasolli, E., Tett, A., Huttenhower, C. and Segata, N., 2015. MetaPhlAn2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling. Nature methods, 12(10), pp.902-903.
centrifuge
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running centrifuge:
Pass the full path to the centrifuge executable in script_path.
Merging of sample centrifuge reports in done with krona. See the section on Parameters that can be set.
Requires
fastq files, either paired end or single:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
Puts the
centrifugeoutput files in:self.sample_data[<sample>]["raw_classification"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["classification"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["classification_report"]
If
ktImportTaxonomy_pathparameter was passed, puts the krona reports inself.sample_data["project_data"]["krona"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
ktImportTaxonomy_path |
Path to ktImportTaxonomy. You can additional |
Lines for parameter file
Centrifuge:
module: centrifuge
base: trim1
script_path: {Vars.paths.centrifuge}
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
ktImportTaxonomy_path: /path/to/ktImportTaxonomy -u http://krona.sourceforge.net
redirects:
--db: /path/to/centrifuge_db
--preload:
--quick:
--threads: 20
References
Kim, D., Song, L., Breitwieser, F. P., & Salzberg, S. L. (2016). Centrifuge: rapid and sensitive classification of metagenomic sequences. Genome research, 26(12), 1721-1729.
Microbiology
CARD_RGI
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running CARD RGI:
RGI is executed on the contigs stored in a Nucleotide fasta file.
Requires
A nucleotide fasta file in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
If
scopeis set tosample:Puts output files in:
sample_data[<sample>]["CARD_RGI.json"]sample_data[<sample>]["CARD_RGI.tsv"]Puts index of output files in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["CARD_RGI.files_index"]If
merge_script_pathis specified in parameters, puts the merged file inself.sample_data["project_data"]["CARD_RGI.merged_reports"]
If
scopeis set toproject:Puts output files in:
sample_data["CARD_RGI.json"]sample_data["CARD_RGI.tsv"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
JSON2tsv_script |
path |
|
merge_script_path |
path |
|
Comments
Lines for parameter file
rgi_inst:
module: CARD_RGI
base: spades1
script_path: python /path/to/rgi.py
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 15
JSON2tsv_script: python /path/to/convertJsonToTSV.py
merge_script_path: Rscript /path/to/merge_reports.R --variable bit_score
orf_to_use: -x
scope: sample
redirects:
-n: 20
-x: 1
References
McArthur, A.G., Waglechner, N., Nizam, F., Yan, A., Azad, M.A., Baylay, A.J., Bhullar, K., Canova, M.J., De Pascale, G., Ejim, L. and Kalan, L., 2013. The comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 57(7), pp.3348-3357.
cgMLST_and_MLST_typing
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad. The MLST typing R script was created by Menachem Sklarz & Michal Gordon
Short Description
A module for a MLST and cgMLST Typing
Requires
- Blast results after parsing in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["blast.parsed"]
Output
- Typing results in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["Typing"]
- Merge of typing results in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["Typing"]
- Files for phyloviz in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["phyloviz_MetaData"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["phyloviz_Alleles"]
- Tree file (if –Tree flag is set) in newick format in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["newick"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
cut_samples_not_in_metadata |
In the final merge file consider only samples found in the Meta-Data file |
|
sample_cutoff |
[0-1] |
In the final merge file consider only samples that have at least this fraction of identified alleles |
Comments
- The following python packages are required:
pandas
- The following R packages are required:
magrittrplyroptparsetools
Note
If using conda environment with R installed the R packages will be automatically installed inside the environment.
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: cgMLST_and_MLST_typing # Name of the module to use
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after steps that generates blast.parsed File_Types]
script_path: # Leave blank
metadata: # Path to Meta-Data file
metadata_samples_ID_field: # Column name in the Meta-Data file of the samples ID
cut_samples_not_in_metadata: # In the final merge file consider only samples found in the Meta-Data file
sample_cutoff: # In the final merge file consider only samples that have at least this fraction of identified alleles
Tree: # Generate newick Tree using hierarchical-clustering [Hamming distance]
Tree_method: # The hierarchical-clustering linkage method [default=complete]
redirects:
--scheme: # Path to the Typing scheme file [Tab delimited]
--Type_col_name: # Column/s name/s in the scheme file that are not locus names
--ignore_unidentified_alleles # Remove columns with unidentified alleles [default=False]
References
Roary
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad. The Bi_clustering R script was created by Eliad Levi
Short Description
A module for running Roary on GFF files
Requires
- For each Sample, GFF file location in:
sample_data[<sample>]["GFF"]
- If there is a GFF directory in the following slot, no new GFF directory will be created and ONLY the GFF files in this directory will be analysed.
sample_data["GFF_dir"]
If the search_GFF flag is on GFF files will be searched in the last base name directory
Output
- puts output GFF directory location in the following slots:
sample_data["GFF"]
- puts output pan_genome results directory location in the following slots:
sample_data["pan_genome_results_dir"]
- puts output pan_genome presence_absence_matrix file location in the following slots:
sample_data["presence_absence_matrix"]
- puts output pan_genome clustered_proteins file location in the following slots:
sample_data["clustered_proteins"]
- puts output GWAS directory location in the following slot:
sample_data["GWAS_results_dir"]
- puts output Biclustering directory location in the following slot:
sample_data["Bicluster_results_dir"]
- puts output Biclustering cluster file location in the following slot:
sample_data["Bicluster_clusters"]
- puts output Gecko directory location in the following slot:
sample_data["Gecko_results_dir"]
- puts Accessory genes or virulence/resistance hierarchical-clustering tree file in the following slot:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["newick"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Comments
- This module was tested on:
Roary v3.10.2Roary v1.006924Scoary v1.6.11Scoary v1.6.9Gecko3
- For the Bi_cluster analysis the following R packages are required:
optparseeisaExpressionViewopenxlsxclusterProfilerorg.Hs.eg.db
- To plot the pan-genome matrix the following python packages are required:
pandaspatsyseabornmatplotlibnumpyscipy
- For the scoary analysis the following python packages are required:
pandas
- For the Gecko analysis the following python packages are required:
pandas
Note
If using conda environment with R installed, the R packages will be automatically installed inside the environment.
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Roary # Name of the module used
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a GFF file generator step like Prokka]
script_path: # Command for running the Roary script
env: # env parameters that needs to be in the PATH for running this module
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
virulence_resistance_tag: # Use the name of the db used in prokka or use "VFDB" if you used the VFDB built-in Prokka module DB
search_GFF: # Search for GFF files?
Bi_cluster: # Do Bi_cluster analysis using the Roary results, if empty or this line dose not exist will not do Bi_cluster analysis
--Annotation: # location of virulence annotation file to use to annotate the clusters or use "VFDB" if you used the VFDB built-in Prokka module DB
--ID_field: # The column name in the MetaData file of the samples IDs
--cols_to_use: # list of the MetaData columns to use to annotate the clusters example: '"ST","CC","source","host","geographic.location","Date"'
--metadata: # location of MetaData file to use to annotate the clusters
plot: # plot gene presence/absence matrix
format: # The gene presence/absence matrix plot output format. example: pdf
Clustering_method # The gene presence/absence matrix plot hierarchical-clustering method. example: ward
Tree: # Save s tree in newick format of the 'Accessory' genes or the 'virulence_resistance_tag' genes hierarchical-clustering
# example: Tree: Accessory
scoary:
script_path: # Command for running the scoary script, if empty or this line dose not exist will not run scoary
BH_cutoff: # Scoary BH correction for multiple testing cut-off
Bonferroni_cutoff: # Scoary Bonferroni correction for multiple testing cut-off
metadata_file: # location of MetaData file to use to create the scoary traits file
metadata_samples_ID_field: # The column name in the MetaData file of the sample's IDs
traits_file: # Path to a traits file
traits_to_pars: # If a traits file is not provided use a list of conditions to create the scoary traits file from MetaData file. example:"source/=='blood'" "source/=='wound'"
# Pairs of field and operator + value to convert to boolean traits: field_name1/op_value1 .. field_nameN/op_valueN Example: "field_1/>=val_1<val_2" "feild_2/=='str_val'"
# A Filter can be used by FILTER_field_name1/FILTER_op_value1&field_name1/op_value1
# Note that Gecko can't run if the Bi_clustering was not run
Gecko:
script_path: # Command for running the Gecko script, if empty or this line dose not exist will not run Gecko
-d: # Parameters for running Gecko
-s: # Parameters for running Gecko
-q: # Parameters for running Gecko
redirects:
-k: # Parameters for running Roary
-p: # Parameters for running Roary
-qc: # Parameters for running Roary
-s: # Parameters for running Roary
-v: # Parameters for running Roary
-y: # Parameters for running Roary
References
Roary program: Page, Andrew J., et al. “Roary: rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis.” Bioinformatics 31.22 (2015): 3691-3693.
Scoary program: Brynildsrud, Ola, et al. “Rapid scoring of genes in microbial pan-genome-wide association studies with Scoary.” Genome biology 17.1 (2016): 238.
Gecko program: Winter, Sascha, et al. “Finding approximate gene clusters with Gecko 3.” Nucleic acids research 44.20 (2016): 9600-9610.
Snippy
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
Short Description
A module for running Snippy on fastq files
Requires
- fastq files in at least one of the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
- puts Results directory location in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["Snippy"]
- puts for each sample the vcf file location in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["vcf"]
- if snippy_core is set to run:
- puts the core Multi-FASTA alignment location in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
- puts core vcf file location of all analyzed samples in the following slot:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["vcf"]- if Gubbins is set to run:
- puts result Tree file location of all analyzed samples in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["newick"]
- update the core Multi-FASTA alignment in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
- update the core vcf file in the slot:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["vcf"]- if pars is set to run, puts phyloviz ready to use files in:
- Alleles:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["phyloviz_Alleles"]
- MetaData:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["phyloviz_MetaData"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Comments
- This module was tested on:
Snippy v3.2gubbins v2.2.0
- For the pars analysis the following python packages are required:
pandas
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Snippy # Name of the module used
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a merge step]
script_path: # Command for running the Snippy script
env: # env parameters that needs to be in the PATH for running this module
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
gubbins:
script_path: # Command for running the gubbins script, if empty or this line dose not exist will not run gubbins
--STR: # More redirects arguments for running gubbins
phyloviz: # Generate phyloviz ready to use files
-M: # Location of a MetaData file
--Cut: # Use only Samples found in the metadata file
--S_MetaData: # The name of the samples ID column
-C: # Use only Samples that has at least this fraction of identified alleles
snippy_core:
script_path: # Command for running the snippy-core script, if empty or this line dose not exist will not run snippy-core
--noref: # Exclude reference
redirects:
--cpus: # Parameters for running Snippy
--force: # Force overwrite of existing output folder (default OFF)
--mapqual: # Minimum mapping quality to allow
--mincov: # Minimum coverage of variant site
--minfrac: # Minumum proportion for variant evidence
--reference: # Reference Genome location
--cleanup # Remove all non-SNP files: BAMs, indices etc (default OFF)
References
- Snippy:
- gubbins:
Croucher N. J., Page A. J., Connor T. R., Delaney A. J., Keane J. A., Bentley S. D., Parkhill J., Harris S.R. “Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins”. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1196, Nucleic Acids Research, 2014
Gubbins
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
Short Description
A module for running Gubbins on a project level nucleotide Multi-FASTA alignment file.
Requires
- Project level nucleotide Multi-FASTA alignment file in the following slot:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
- puts result Tree file location of all analyzed samples in the slot:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["newick"]
- update the Multi-FASTA alignment in the slot:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
- puts the filtered vcf file in the slot:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["vcf"]
- if pars is set to run, puts phyloviz ready to use files in the slots:
- Alleles:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["phyloviz_Alleles"]
- MetaData:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["phyloviz_MetaData"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Comments
- This module was tested on:
gubbins v2.2.0
- For the pars analysis the following python packages are required:
pandas
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Gubbins # Name of the module used
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after a step that generates a Project level nucleotide Multi-FASTA alignment]
script_path: # Command for running the gubbins script, if empty or this line dose not exist will not run gubbins
env: # env parameters that needs to be in the PATH for running this module
qsub_params:
-pe: # Number of CPUs to reserve for this analysis
phyloviz: # Generate phyloviz ready to use files
-M: # Location of a MetaData file
--Cut: # Use only Samples found in the metadata file
--S_MetaData: # The name of the samples ID column
-C: # Use only Samples that has at least this fraction of identified alleles
redirects:
--threads: # Parameters for running Gubbins
References
- gubbins:
Croucher N. J., Page A. J., Connor T. R., Delaney A. J., Keane J. A., Bentley S. D., Parkhill J., Harris S.R. “Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins”. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1196, Nucleic Acids Research, 2014
Tree_plot
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
Short Description
A module for plotting tree file in newick format together with MetaData information and possible additional matrix information.
Requires
- A tree file in newick format in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["newick"]
- Tab delimited file with samples names in one of the columns from:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["MetaData"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["results"]or from external file.
Output
Generate pdf file of the tree with the MetaData information:
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Comments
- The following R packages are required:
optparseapeggtreeopenxlsx
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Tree_plot # Name of the used module
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after and generate a Tree plot [must be after a tree making step]
# If more then one base is specified: the first overwrite the other bases overlapped slots
script_path: # Command for running the Tree plot script
# If this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
iterate_on_bases: # If set will iterate over the step's bases and generate a plot for each base.
tree_by_heatmap: # Generate additional tree using Hierarchical Clustering of the heatmap
redirects:
--layout: # Tree layout [fan or rectangular (default)]
--Meta_Data: # Path to tab-delimited Meta Data file with header line.
# If this line is empty or missing it will try searching for results data.
--M_Excel: # If the Meta_Data input is an Excel file indicate the sheet name to use
--ID_field: # Column name in the Meta Data file for IDs found in the tips of the tree
--cols_to_use: # Columns in the Meta Data file to use and the order from the center up
--open.angle: # Tree open angle.
--branch.length: # Don't use branch length [cladogram]
--conect.tip: # Connect the tip to its label
--pre_spacer: # Space before the label text [default=0.05]
--post_spacer: # Space after the label text [default=0.01]
--OTU: # Column name in the Meta Data file to use as OTU annotation
--labels: # Use branch length labels
--Tip_labels: # Show tip labels
--heatmap: # Path to Data file to generate a heatmap
# If this line is empty it will try searching for results data.
--H_Excel: # If the heatmap input is an Excel file indicate the sheet name to use
--heatmap_cell_border: # Color of heatmap cell border [default='white']
--heatmap_lowest_value: # Color of heatmap lowest value [default='white']
--heatmap_highest_value: # Color of heatmap highest value [default='red']
--cols_to_use_heatmap: # Columns in the heatmap Data file to use and the order from the center up
--ID_heatmap_field: # Column name for IDs found in the tips of the tree in the heatmap Data file
--heatmap_variable: # Use only variable columns in the heatmap
--heatmap_count_by_sep: # Count the sep in each cell to generate the values for the heatmap
--heatmap_HC_dist: # The heatmap Hierarchical Clustering dist method
--heatmap_HC_agg: # The heatmap Hierarchical Clustering agglomeration method
QIIME (version 1.9)
Modules included in this section
qiime_prep
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for preparing fastq reads for analysis with QIIME (1.9):
The reads stored in each sample are optinally joined and then set it a directory in such a way the downstream, QIIME’s demult can concatenate the sequences while saving the sample of origin.
The directory will contain symbolic links to the files to be used by demult in the following step.
Requires
fastq files in one of the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
Output
Puts directory of links to files to use with QIIME:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["qiime.prep_links_dir"]
If join is performed:
puts the new joined reads in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.J"]
puts the unjoined forward reads in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F"]
puts the unjoined reverse reads in:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.R"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
join |
none, join (or join_cat - not implemented) |
Wheather to join paired reads. |
unjoined |
forward, reverse, both or none |
What to do with unjoined sequences? Use only forward, only reverse, both or none. If join is none, use this parameter to indicate which reads to take for analysis. |
join_algo |
forward, reverse, both or none |
What to do with unjoined sequences? |
parameters |
Path to QIIME parameter file to be used downstream |
Lines for parameter file
q_prep_1:
module: qiime_prep
base: merge1
script_path: /path/to/join_paired_ends.py
join: join
unjoined: forward
parameters: /path/to/qiime_params.txt
redirects:
--pe_join_method: fastq-join
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_demult
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s multiple_split_libraries_fastq.py:
The reads from step qiime_prep are combined into one seqs.fna file.
Note
The module has not been tested on other types of data, such as undemultiplexed reads. It should work but there will probably be unexpected problems.
Requires
A directory of read files with smaple names coded in the file names, such as the directory produced by qiime_prep:
sample_data["qiime.prep_links_dir"]
Output
Puts the resulting
seqs.fnafile in the following slots:self.sample_data["project_data"]["qiime.demult_seqs"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["qiime.fasta"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
Lines for parameter file
q_demult_1:
module: qiime_demult
base: q_prep_1
script_path: '/path/to/multiple_split_libraries_fastq.py'
redirects:
--demultiplexing_method: sampleid_by_file
--include_input_dir_path: null
--parameter_fp: /path/to/qiime_params
--remove_filepath_in_name: null
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_chimera
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s identify_chimeric_seqs.py:
The module can operate on the raw seqs.fna or on an aligned version. The latter is used for ChimeraSlayer and the former for usearch61
Requires
A fasta file in:
sample_data["qiime.fasta"]
Alternatively, an aligned fasta file in:
sample_data["fasta.aligned"]
Output
Puts the resulting list of chimeras in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["chimeras"]
Puts the filtered fasta file in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.chimera_removed"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
Note
When using parallel_identify_chimeric_seqs.py, the module tries to build the scripts appropriately. It is wise to check the parallel scripts before running them…
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
method |
usearch61 or ChimeraSlayer |
Method to use for the analysis (passed to the –chimera_detection_method of |
Lines for parameter file
q_chimera_usrch:
module: qiime_chimera
base: q_demult_1
# script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/parallel_identify_chimeric_seqs.py'
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/identify_chimeric_seqs.py'
method: usearch61 # Or ChimeraSlayer. Will guess depending on existing files.
redirects:
# --jobs_to_start: 20
--aligned_reference_seqs_fp: /path/to/reference_files.otus_aligned
--reference_seqs_fp: /path/to/reference_files.otus
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_pick_otus
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s pick_otus.py
Requires
A fasta file in:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
Puts the resulting OTU table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["otu_table"]
Lines for parameter file
q_pick_otu_1:
module: qiime_pick_otus
base: q_chimera_usrch
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/pick_otus.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_pick_rep_set
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s pick_rep_set.py
Requires
A fasta file in:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
An OTU table in:
sample_data["otu_table"]
Output
Puts the resulting fasta file in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
Saves the original fasta file in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["qiime.full_fasta"]
Lines for parameter file
q_rep_set_1:
module: qiime_pick_rep_set
base: q_pick_otu_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/pick_rep_set.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_align_seqs
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME's align_seqs.py:
Can be used for the parallel versions thereof: parallel_align_seqs_pynast.py
Requires
A fasta file in:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
Puts the resulting aligned fasta file in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.aligned"]
Stores the old, unaligned version in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.unaligned"]
Note
When using parallel_align_seqs_pynast.py, the module tries to build the scripts appropriately. It is wise to check the parallel scripts before running them…
Lines for parameter file
q_align_para:
module: qiime_align_seqs
base: q_rep_set_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/parallel_align_seqs_pynast.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
redirects:
--jobs_to_start: 5
--retain_temp_files:
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_filter_alignment
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s filter_alignment.py
Requires
A fasta file in:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
Puts the resulting aligned fasta file in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
Saves the original unaligned fasta file in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.aligned_unfiltered"]
Lines for parameter file
q_filt_align_1:
module: qiime_filter_alignment
base: q_align_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/filter_alignment.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_assign_taxonomy
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s assign_taxonomy.py
Can also be used to run the parallel versions of the program:
parallel_assign_taxonomy_blast.py
parallel_assign_taxonomy_rdp.py
parallel_assign_taxonomy_uclust.py
Requires
A fasta file in:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
Puts the resulting list of chimeras in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["taxonomy"]
Note
When using the parallel version, the module tries to build the scripts appropriately. It is wise to check the parallel scripts before running them…
Lines for parameter file
q_tax_asn_1:
module: qiime_assign_taxonomy
base: q_rep_set_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/parallel_assign_taxonomy_rdp.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
redirects:
--confidence: 0.5
--id_to_taxonomy_fp: {Vars.reference_files.id_to_taxonomy}
--jobs_to_start: 20
--rdp_max_memory: 50000
--reference_seqs_fp: {Vars.reference_files.otus}
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_make_phylogeny
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s make_phylogeny.py
Requires
A fasta file in:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
Puts the resulting OTU table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["phylotree"]
Lines for parameter file
q_phylo_1:
module: qiime_make_phylogeny
base: q_filt_align_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/make_phylogeny.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_make_otu_table
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s make_otu_table.py:
The module creates a BIOM table based on the OTU table and a taxonomy assignment if avaliable (will be available if the qiime_assign_taxonomy is in the branch).
If chimera checking has been performed, the suspected chimeric sequences will be removed from the BIOM table.
The module also adds code for creating a summary of the BIOM table and a tab-delimited version thereof.
Requires
An OTU table:
sample_data["otu_table"]
Optional
A taxonomy assignment of the sequences:
sample_data["taxonomy"]
Output
Puts the BIOM table in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table"]
Puts the BIOM table summary in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_summary"]
Puts the BIOM table in tab-delimited format in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_tsv"]
If a fasta.chimera_removed file exists, will put the unfiltered BIOM table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["unfiltered_biom_table"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
skip_summary |
If passed, will not create the BIOM table summary. |
|
skip_tsv |
If passed, will not create the tsv version of the BIOM table. |
Lines for parameter file
q_mk_otu_1:
module: qiime_make_otu_table
base: q_phylo_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/make_otu_table.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
# skip_summary:
# skip_tsv:
redirects:
--mapping_fp: /path/to/qiime1_mapping.txt
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_filter_samples_from_otu_table
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s filter_samples_from_otu_table.py
Requires
A BIOM table in:
sample_data["biom_table"]
Output
Puts the resulting BIOM table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table"]
Puts the BIOM table summary in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_summary"]
Puts the BIOM table in tab-delimited format in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_tsv"]
Puts the unfiltered BIOM table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["prefilter_biom_table"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
skip_summary |
If passed, will not create the BIOM table summary. |
|
skip_tsv |
If passed, will not create the tsv version of the BIOM table. |
Lines for parameter file
filt_samp_1:
module: qiime_filter_samples_from_otu_table
base: q_mk_otu_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/filter_samples_from_otu_table.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
redirects:
--mapping_fp: /path/to/mapping.txt
--min_count: 100000
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_filter_otus
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s filter_otus_from_otu_table.py
Requires
A BIOM table in:
sample_data["biom_table"]
Output
Puts the resulting BIOM table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table"]
Puts the BIOM table summary in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_summary"]
Puts the BIOM table in tab-delimited format in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_tsv"]
Puts the unfiltered BIOM table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["prefilter_biom_table"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
skip_summary |
If passed, will not create the BIOM table summary. |
|
skip_tsv |
If passed, will not create the tsv version of the BIOM table. |
Lines for parameter file
q_filt_otus_1:
module: qiime_filter_otus
base: filt_samp_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/filter_otus_from_otu_table.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
redirects:
--min_count_fraction: 0.00005
--min_samples: 10
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_sort_otu_table
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s sort_otu_table.py
Requires
A BIOM table in:
sample_data["biom_table"]
Output
Puts the resulting BIOM table in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table"]
Puts the BIOM table summary in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_summary"]
Puts the BIOM table in tab-delimited format in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["biom_table_tsv"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
skip_summary |
If passed, will not create the BIOM table summary. |
|
skip_tsv |
If passed, will not create the tsv version of the BIOM table. |
Lines for parameter file
q_sort_otus_1:
module: qiime_sort_otu_table
base: filt_samp_1
script_path: '{Vars.qiime_path}/sort_otu_table.py'
setenv: {Vars.qiime_env}
redirects:
--sort_field: XXX
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
qiime_divers
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
A module for running QIIME’s core_diversity_analyses.py:
The module creates a BIOM table based on the OTU table and a taxonomy assignment if avaliable (will be available if the qiime_assign_taxonomy is in the branch).
If chimera checking has been performed, the suspected chimeric sequences will be removed from the BIOM table.
The module also adds code for creating a summary of the BIOM table and a tab-delimited version thereof.
Requires
A BIOM table:
sample_data["biom_table"]
Optional
A phylogenetic tree:
sample_data["phylotree"]
Output
Puts the core diversity directory name in
self.sample_data["project_data"]["diversity"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
–mapping_fp |
A path to the qiime mapping file (if not set, will use the mapping file passed in |
|
–parameter_fp |
A path to a qiime parameter file. |
Lines for parameter file
q_divers_1:
module: qiime_divers
base: q_filt_otus_1
script_path: /path/to/QIIME/bin/core_diversity_analyses.py
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
sampling_depth: 109897
redirects:
--categories: Disease,sex
--parameter_fp: /path/to/parameter_file
References
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I. and Huttley, G.A., 2010. “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data”. Nature methods, 7(5), pp.335-336.
QIIME (version 2)
Modules included in this section
Note
The modules were tested on qiime version 2018.11
qiime2_import
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running qiime tools import on various importable types
Note
Tested on qiime2 version 2018.11
Requires
If importing reads:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.F|R|S"]
If importing other types, requires that type in the sample file
The file can be defined in the sample file either just as a path, or as a path, format pair, as follows:
Only path:
EMPSingleEndSequences /path/to/emp-single-end-sequences
Path, format pair:
EMPSingleEndSequences /path/to/emp-single-end-sequences EMPSingleEndSequences EMPPairedEndDirFmt
Output:
If importing reads, will create the imported artifact in one of:
sample_data["project_data"]["SampleData[SequencesWithQuality]"]sample_data["project_data"]["SampleData[PairedEndSequencesWithQuality]"]
If importing other types:
sample_data["project_data"]["<type imported>"]
Parameters that can be set
Lines for parameter file
Importing paired end reads:
import_reads:
module: qiime2_import
base: trim1
script_path: qiime tools import
redirects:
--type: SampleData[PairedEndSequencesWithQuality]
--input-format: PairedEndFastqManifestPhred33
Importing internal types:
merge_data:
module: Import
src: EMPSingleEndSequences
trg: EMPSingleEndSequences
script_path: ..import..
scope: project
import:
module: qiime2_import
base: merge_data
script_path: qiime tools import
References
Bolyen, E., Rideout, J.R., Dillon, M.R., Bokulich, N.A., Abnet, C., Al-Ghalith, G.A., Alexander, H., Alm, E.J., Arumugam, M. and Asnicar, F., 2018. QIIME 2: Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science. PeerJ Preprints 6:e27295v1 https://doi.org/10.7287/peerj.preprints.27295v1
qiime2_general
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Attention
This module is in Beta version. It is not issue-free and will be improved periodically.
A module to include any QIIME2 plugin method, pipeline or visualiation.
The required plugin and method are specified in the script_path line, as they would appear in the command line, e.g.:
script_path: qiime dada2 denoise-paired
The module will identify the required inputs for the method and extract them from the appropriate slots. If they are not found, an exception will be thrown.
If more than one type is legitimate fdr a method, and both exist in the project, NeatSeq-Flow will complain. You can
either remove the extra type with manage_types module or specify the type to use with the type parameter.
Plugins which require metadata files, passed as argument --m-metadata-file, will look for a file in slot metadata.
In order to specify a metadata file in the parameter file, pass the --m-metadata-file in the redirects section.
All redirects argument values are searched for in the “project_data”. Thus, you can specify slots to use for
redirected arguments.
Requires
Plugin- and method-specific.
Output:
Plugin- and method-specific.
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
store_output |
list of output parameters |
These parameters will be stored as file types for use by downstream modules |
export_o_params |
empty or list of output parameters |
If empty, all outputs will be exported, i.e. unzipped with qiime tools export. If list of parameters, only those types will be exported. |
Lines for parameter file
DADA2 plugin, with export of stats output:
dada2: # Name of this step
module: qiime2_general
base: import
script_path: qiime dada2 denoise-single #paired
export_o_params:
- --o-denoising-stats
redirects:
--p-trim-left: 10
--p-trunc-len: 100
Classical visualization. Only base and script_path:
dada2_vis_summary: # Name of this step
module: qiime2_general
base: dada2
script_path: qiime feature-table summarize
Store only particular outputs in type index:
diversity: # Name of this step
module: qiime2_general
base: phylogeny
script_path: qiime diversity core-metrics-phylogenetic
export_o_params: --o-rarefied-table
store_output:
- --o-rarefied-table
- --o-faith-pd-vector
- --o-weighted-unifrac-distance-matrix
- --o-weighted-unifrac-pcoa-results
- --o-weighted-unifrac-emperor
redirects:
--p-sampling-depth: 50000
taxonomy_tabulate: # Name of this step
module: qiime2_general
base: taxonomy
script_path: qiime metadata tabulate
redirects:
--m-input-file: "{{FeatureData[Taxonomy]}}"
References
Bolyen, E., Rideout, J.R., Dillon, M.R., Bokulich, N.A., Abnet, C., Al-Ghalith, G.A., Alexander, H., Alm, E.J., Arumugam, M. and Asnicar, F., 2018. QIIME 2: Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science. PeerJ Preprints 6:e27295v1 https://doi.org/10.7287/peerj.preprints.27295v1
GATK
Modules included in this section
GATK_CatVariants
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module to concatenate chromosome to get one VCF file for each sample.
Attention
The module generate script for each sample - chromosom.
The programs included in the module are the following:
CatVariants(GATK)
Requires
self.sample_data[sample][chr]["GATK_vcf"]
Output
self.sample_data[sample]["vcf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
||
chrom_list |
Comma-separated list of chromosome names as mentioned in the BAM file |
Lines for parameter file
GATK_CatVariants1:
module: GATK_CatVariants
base: GATK_SelectVariants_VEPfiltered
script_path: /path/to/java -cp /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar org.broadinstitute.gatk.tools.CatVariants
genome_reference: /path/to/gatk/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
References
Van der Auwera, Geraldine A., et al. “From FastQ data to high‐confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline.” Current protocols in bioinformatics 43.1 (2013): 11-10.
GATK_gvcf
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for generate gVCF file from BAM file.
Attention
The module generate script for each sample-chromosom.
The programs included in the module are the following:
HaplotypeCaller(GATK)
Requires
self.sample_data[sample]["bam"]
Output
self.sample_data[sample][chr]["GATK_g.vcf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
||
chrom_list |
Comma-separated list of chromosome names as mentioned in the BAM file |
Lines for parameter file
GATK_gvcf: # check about -nct for parallization and deal with memmory problem
module: GATK_gvcf
base: GATK_pre_processing
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar
genome_reference: /path/to/gatk/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 15
redirects:
-nct: 15
References
Van der Auwera, Geraldine A., et al. “From FastQ data to high‐confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline.” Current protocols in bioinformatics 43.1 (2013): 11-10.
GATK_hard_filters
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for apply hard filters to a variant callset that is too small for VQSR or for which truth/training sets are not available..
Attention
The module generate script for each chromosom.
The programs included in the module are the following:
SelectVariants and VariantFiltration(GATK)
Requires
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Output
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
||
chrom_list |
Comma-separated list of chromosome names as mentioned in the BAM file |
|
filterExpression_SNP |
filter e xpression for SNP |
|
filterExpression_INDEL |
filter e xpression for INDEL |
Lines for parameter file
GATK_hard_filters1:
module: GATK_hard_filters
base: GenotypeGVCFs1
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar
genome_reference: /path/to/gatk/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
filterExpression_SNP: '"QD < 2.0 || MQ < 40.0 || FS > 60.0 || SOR > 3.0 || MQRankSum < -12.5 || ReadPosRankSum < -8.0"'
filterExpression_INDEL: '"QD < 2.0 || ReadPosRankSum < -20.0 || FS > 200.0 || SOR > 10.0 || InbreedingCoeff < -0.8"'
References
Van der Auwera, Geraldine A., et al. “From FastQ data to high‐confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline.” Current protocols in bioinformatics 43.1 (2013): 11-10.
GATK_merge_gvcf
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for combine g.vcf files to cohorts.
Attention
The module generate script for each sample-chromosom.
The programs included in the module are the following:
CombineGVCFs(GATK)
Requires
self.sample_data[sample][chr]["GATK_g.vcf"]
Output
self.sample_data["cohorts"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
||
chrom_list |
Comma-separated list of chromosome names as mentioned in the BAM file |
|
cohort_size |
number of g.vcf file to be in each cohort |
Lines for parameter file
gatk_merge_gvcf:
module: GATK_merge_gvcf
base: GATK_gvcf
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar
genome_reference: /path/to/gatk/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
cohort_size: 10
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
References
Van der Auwera, Geraldine A., et al. “From FastQ data to high‐confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline.” Current protocols in bioinformatics 43.1 (2013): 11-10.
GATK_pre_processing
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for generating ready-to-GATK-use BAM files from fastq files.
Attention
The module lacks the “base recalibration process (BQSR)” step
The programs included in the module are the following:
FastqToSamPicard tool to generate uBAMMarkIlluminaAdaptersPicard tool to Mark Illumina AdaptersSamToFastqPicard tool uBAM to fastqMergeBamAlignmentPicard tool to merge BAM and uBAMMarkDuplicatesPicard tool to remove PCR duplicatesBWA MEMmapping with BWA MEM
Requires
A fastq file in the following locations:
self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.F"]self.sample_data[sample]["fastq.R"]
Output
self.sample_data[sample]["bam"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
picard_path |
path to PICARD |
Full path to the PICARD .jar file |
bwa_mem_path |
||
genome_reference |
Lines for parameter file
GATK_pre_processing:
module: GATK_pre_processing
base: fQC_trim
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar
picard_path: /path/to/picard.jar
bwa_mem_path: /path/to/bwa mem
genome_reference: /path/to/gatk/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
threads: 20
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
References
GATK_SelectVariants
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for separation of multi-VCF per-chromosome to one VCF per-sample per-chromosome
Attention
The module generates a script for each sample/chromosome.
The programs included in the module are the following:
SelectVariants(GATK)
Requires
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Output
self.sample_data[sample][chr]["GATK_vcf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
path to reference genome |
|
chrom_list |
Comma-separated list of chromosome names as mentioned in the BAM file |
Lines for parameter file
GATK_SelectVariants_VEPfiltered:
module: GATK_SelectVariants
base: VEP1
script_path: /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
genome_reference: /path/to/gatk/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
redirects:
--setFilteredGtToNocall: null
References
Van der Auwera, Geraldine A., et al. “From FastQ data to high‐confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline.” Current protocols in bioinformatics 43.1 (2013): 11-10.
GATK_VQSR
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for apply VQSR filters
Attention
The module generates script for each chromosoms.
The programs included in the module are the following:
VariantRecalibratorandApplyRecalibration(GATK)
Requires
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Output
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
||
chrom_list |
list of chromosomes names as mentioned in BAM file separated by ‘,’ |
|
ts_filter_level_SNP |
filter e xpression for SNP |
|
ts_filter_level_INDEL |
filter e xpression for INDEL |
|
resource_SNP |
||
resource_INDEL |
Lines for parameter file
GATK_VQSR1:
module: GATK_VQSR
base: GenotypeGVCFs1
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar
genome_reference: /path/to/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
resource_SNP:
- hapmap,known=false,training=true,truth=true,prior=15.0 /path/to/bundle/b37/hapmap_3.3.b37.vcf
- omni,known=false,training=true,truth=true,prior=12.0 /path/to/bundle/b37/1000G_omni2.5.b37.vcf
- 1000G,known=false,training=true,truth=false,prior=10.0 /path/to/bundle/b37/1000G_phase1.snps.high_confidence.b37.vcf
- dbsnp,known=true,training=false,truth=false,prior=2.0 /path/to/bundle/b37/dbsnp_138.b37.vcf
resource_INDEL:
- mills,known=false,training=true,truth=true,prior=12.0 /path/to/bundle/b37/Mills_and_1000G_gold_standard.indels.b37.sites.vcf
- dbsnp,known=true,training=false,truth=false,prior=2.0 /path/to/bundle/b37/dbsnp_138.b37.vcf
ts_filter_level_SNP: 99.0
ts_filter_level_INDEL: 99.0
maxGaussians: 4
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
References
Van der Auwera, Geraldine A., et al. “From FastQ data to high‐confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline.” Current protocols in bioinformatics 43.1 (2013): 11-10.
GenotypeGVCFs
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for perform joint genotyping on gVCF files produced by HaplotypeCaller.
Attention
The module generate script for each cohort-chromosom.
The programs included in the module are the following:
GenotypeGVCFs(GATK)
Requires
self.sample_data["cohorts"]
Output
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
||
chrom_list |
list of chromosomes names as mentioned in BAM file separated by ‘,’ |
Lines for parameter file
GenotypeGVCFs1:
module: GenotypeGVCFs
base: gatk_merge_gvcf
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/GenomeAnalysisTK.jar
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
genome_reference: /path/to/gatk/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
References
Van der Auwera, Geraldine A., et al. “From FastQ data to high‐confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline.” Current protocols in bioinformatics 43.1 (2013): 11-10.
Picard_CollectAlignmentSummaryMatrics
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for statistical information about the mapping generated by CollectAlignmentSummaryMetrics from Picard tools.
The programs included in the module are the following:
CollectAlignmentSummaryMatricsfrom PICARD tools.
Requires
A fastq file in the following location:
self.sample_data[sample]["bam"]
Output
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
genome_reference |
Lines for parameter file
Picard_CollectAlignmentSummaryMatrics1:
module: Picard_CollectAlignmentSummaryMatrics
base: GATK_pre_processing
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/picard-1.139/dist/picard.jar
genome_reference: /path/to/bundle/b37/human_g1k_v37_decoy.fasta
References
Picard_CollectVariantCalling
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for generating SNP and indel statistics information
The programs included in the module are the following:
CollectVariantCallingMetricsPicard tool to generate A collection of metrics relating to snps and indels within a variant-calling file (VCF)
Requires
A fastq file in the following location:
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Output
Lines for parameter file
Picard_CollectVariantCalling1:
module: Picard_CollectVariantCalling
base: GATK_hard_filters1
script_path: /path/to/java -jar /path/to/picard.jar
DBSNP: /path/to/bundle/b37/dbsnp_138.b37.vcf
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
References
VEP
- Authors
Michal Gordon
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for annotation of the multi VCF file
Attention
The module generates a script for each chromosome.
The programs included in the module are the following:
VEP(Variant Effect Predictor. )
Requires
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]
Output
self.sample_data[chr]["vcf"]- annotated multi-VCF per chromosome
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
chrom_list |
Comma-separated list of chromosome names as mentioned in the BAM file |
Note
VEP parameters can be passed via redirects
Lines for parameter file
VEP1:
module: VEP
base: GATK_hard_filters1
script_path: /path/to/vep
chrom_list: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, X, Y, MT"
redirects:
--format: vcf
--offline: null
--species: homo_sapiens
--fork: 10
--assembly: GRCh37
--max_af: null
--pick: null
--dir: /path/to/VEP/ensembl-vep-release-88.10/cache
--check_existing: null
--symbol: null
--force_overwrite: null
--vcf: null
References
McLaren, William, et al. “The ensembl variant effect predictor.” Genome biology 17.1 (2016): 122.
Sequence Clustering
Modules included in this section
cd_hit
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for clustering with cd-hit/ch-hit-est:
This module runs both cd-hit and cd-hit-est. The type of sequence (nucl or prot) will be determined by the program supplied in script_path.
You must make sure that the required file exists: If clustering prot sequences with cd-hit-est, make sure there is a fasta.prot file, etc.
CD-HIT: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences, Weizhong Li & Adam Godzik. Bioinformatics, (2006) 22:1658-1659
CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next generation sequencing data, Limin Fu, Beifang Niu, Zhengwei Zhu, Sitao Wu & Weizhong Li. Bioinformatics, (2012) 28:3150-3152
Requires
fasta files in the following slot (scope = sample):
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"|"fasta.prot"]
fasta files in the following slot (scope = project):
sample_data["fasta.nucl"|"fasta.prot"]
Output
Puts the output fasta file in the fasta slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"|"fasta.prot"]Or
self.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"|"fasta.prot"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project or sample fasta. |
Lines for parameter file
clust_proj:
module: cd_hit
base: derepel_proj
script_path: 'path/to/cd-hit-est'
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 40
scope: project
redirects:
-T: 40
References
Fu, L., Niu, B., Zhu, Z., Wu, S. and Li, W., 2012. CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics, 28(23), pp.3150-3152.
vsearch_cluster
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running vsearch clustering:
The reads stored in fasta files are clustered with one of the 3 methods available: cluster_fast, cluster_size or cluster_smallmem.
..Note: At the moment this works on the nucl fasta only. See the web: https://github.com/torognes/vsearch/issues/42
Output types are defined with the outputs parameter which can be a comma separated list of the following:
biomout,mothur_shared_out,otutabout,profile,uc
Fasta output files are defined with the fasta_outputs parameter which can be a comma separated list of the following:
centroids,consout,msaout
By default, the centroids file is stored in the fasta slot. Change this by setting store_fasta to one of the types listed above, i.e. centroids,consout or msaout
Requires
fasta files in the following slot (scope = sample):
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
fasta files in the following slot (scope = project):
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]
Output
Puts required output in similarly named slots, e.g.:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["vsearch.centroids"]orself.sample_data["project_data"]["vsearch.centroids"]Puts the required fasta in the fasta slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]orself.sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
outputs |
biomout,mothur_shared_out,otutabout,profile,uc |
List of outputs other than fasta type outputs (see fasta_outputs |
fasta_outputs |
centroids,consout,msaout |
A list of fasta types to produce. |
store_fasta |
centroids|consout|msaout |
The fasta type to store in fasta slot |
scope |
project | sample |
Indicates whether to use a project or sample nucl fasta. |
Lines for parameter file
clust_proj:
module: vsearch_cluster
base: derepel_proj
script_path: '{Vars.vsearch_path}/vsearch'
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 40
fasta_outputs: centroids,consout
outputs: uc
store_fasta: centroids
scope: project
type: cluster_fast
redirects:
--id: 0.85 # From ipyrad defaults
--qmask: dust
--strand: both
--threads: 40
--sizein:
--sizeout:
References
Rognes, T., Flouri, T., Nichols, B., Quince, C. and Mahé, F., 2016. VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ, 4, p.e2584.
vsearch_derepel
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running vsearch read dereplication:
Performs dereplication on fastq and fasta files.
Note
Dereplication with vsearch is not defined on paired end reads.
At the moment, this module is defined only for fasta.nucl or for fastq.S.
Requires
fastq files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fastq.S"]
or fasta files the following slot:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]
Output
Puts output fasta file in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]self.sample_data[<sample>]["vsearch_derepl"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample | project |
Which file to use for dereplication: sample-wise or project-wise files |
uc |
Save UCLUST-like dereplication output? (see –uc in manual) |
|
type |
derep_fulllength | derep_prefix |
Type of derelpication strategy. See manual |
Lines for parameter file
For external index:
derepel_proj:
module: vsearch_derepel
base: merge_proj
script_path: '{Vars.vsearch_path}/vsearch'
scope: project
type: derep_fulllength
uc:
redirects:
--sizein:
--sizeout:
References
Rognes, T., Flouri, T., Nichols, B., Quince, C. and Mahé, F., 2016. VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ, 4, p.e2584.
Various Reporting Programs
Modules included in this section
NGSplot
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for running NGSplot:
Runs NGSplot on existing sorted BAM files.
Please make sure the BAM is sorted, such as following the samtools module
If this is a ChIP-seq experiment and you have controls defined, it will also run NGSplot for the sample:control comparison.
At the moment, the module works only at the sample scope. (BAM files in the project scope are rare!)
Requires
BAM files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["bam"]
Output
Puts output NGS reports in the following slots:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["NGSplot"]
For ChIP-seq data, puts comparison reports in
self.sample_data[<sample>]["NGSplot_vs_control"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
setenv |
NGSPLOT=/path/to/ngsplot |
Running NGSplot requires setting this EV. |
Lines for parameter file
NGSplot_genebody:
module: NGSplot
base: sam_base
script_path: Rscript /path/to/ngsplot-2.61/bin/ngs.plot.r
setenv: NGSPLOT=/path/to/ngsplot-2.61
redirects:
-G: mm10
-R: genebody
-P: 20
-GO: hc
qsub_params:
-pe: shared 20
References
Shen, L., Shao, N., Liu, X. and Nestler, E., 2014. ngs.plot: Quick mining and visualization of next-generation sequencing data by integrating genomic databases. BMC genomics, 15(1), p.284.
Multiqc *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for preparing a MultiQC report for all samples.
Tip
By default, the module will search for parsable reports in the directories of all the modules in the branch leading to this instance. To search only in the directories of the explicit base steps, specify the bases_only parameter.
Requires
No real requirements. Will give a report with information if one of the base steps produces reports that MultiQC can read, e.g. fastqc, bowtie2, samtools etc.
Output
puts report dir in the following slot:
self.sample_data[<sample>]["Multiqc_report"]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
bases_only |
Search directories of explicit base steps only. |
Lines for parameter file
firstMultQC:
module: Multiqc
base:
- sam_bwt2_1
- fqc_trim1
bases_only:
script_path: /path/to/multiqc
References
Ewels, P., Magnusson, M., Lundin, S. and Käller, M., 2016. MultiQC: summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics, 32(19), pp.3047-3048.
Collect_results
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
Short Description
A module to Collect and merge/append results from all base steps directories: This module will search for each base step for all the results files with a common name pattern [Regular expression]. The search will be done within the base step result directories. The sample name could be inferred for each result file base on the parent directory name and added to the merged file [as new column named “Samples”]. All the results files will be append [by default] or merged by a common column name. The merge files can then be convert individually to pivot table file
Requires
Tab delimited files with common name pattern found within the base step data directories:
For example files ending with .out
Output
Generate merged tab delimited files:
Will generate file for each of the base steps with the file ending with .merg
Can also generate Excel file with sheet for each base step
- Put results file in:
self.sample_data[“project_data”][“results”]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Comments
- The following python packages are required:
pandasopenpyxl
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Collect_results # Name of the used module
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after and collect results from [must be after a merge step]
script_path: # Command for running the a merging script
# If this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
redirects:
-R: # Regular expression to find result files
--Merge_by: # Merge files by common column
--header: # Don't use a header row, use integers instead [0,1,2,3...], easy to use with --pivot option
--Excel: # Collect all results to excel file split by sheets
--add_samples_names: # Infer and add samples names from file parent directory to "Samples" column
--pivot: # Convert to pivot table by [index columns values]
# If with the options: -add_samples_names and --header it is possible to use: '''Samples'' '5' '0''
--MetaData: # Use external MetaData file as the base for merging
--split_by: # Split the data in the columns [index <columns> values] before pivot
--sep: # Columns separator for input file
-T: # Write Transpose output
Tree_plot
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Note
This module was developed as part of a study led by Dr. Jacob Moran Gilad
Short Description
A module for plotting tree file in newick format together with MetaData information and possible additional matrix information.
Requires
- A tree file in newick format in:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["newick"]
- Tab delimited file with samples names in one of the columns from:
self.sample_data["project_data"]["MetaData"]self.sample_data["project_data"]["results"]or from external file.
Output
Generate pdf file of the tree with the MetaData information:
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Comments
- The following R packages are required:
optparseapeggtreeopenxlsx
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Tree_plot # Name of the used module
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after and generate a Tree plot [must be after a tree making step]
# If more then one base is specified: the first overwrite the other bases overlapped slots
script_path: # Command for running the Tree plot script
# If this line is empty or missing it will try using the module's associated script
iterate_on_bases: # If set will iterate over the step's bases and generate a plot for each base.
tree_by_heatmap: # Generate additional tree using Hierarchical Clustering of the heatmap
redirects:
--layout: # Tree layout [fan or rectangular (default)]
--Meta_Data: # Path to tab-delimited Meta Data file with header line.
# If this line is empty or missing it will try searching for results data.
--M_Excel: # If the Meta_Data input is an Excel file indicate the sheet name to use
--ID_field: # Column name in the Meta Data file for IDs found in the tips of the tree
--cols_to_use: # Columns in the Meta Data file to use and the order from the center up
--open.angle: # Tree open angle.
--branch.length: # Don't use branch length [cladogram]
--conect.tip: # Connect the tip to its label
--pre_spacer: # Space before the label text [default=0.05]
--post_spacer: # Space after the label text [default=0.01]
--OTU: # Column name in the Meta Data file to use as OTU annotation
--labels: # Use branch length labels
--Tip_labels: # Show tip labels
--heatmap: # Path to Data file to generate a heatmap
# If this line is empty it will try searching for results data.
--H_Excel: # If the heatmap input is an Excel file indicate the sheet name to use
--heatmap_cell_border: # Color of heatmap cell border [default='white']
--heatmap_lowest_value: # Color of heatmap lowest value [default='white']
--heatmap_highest_value: # Color of heatmap highest value [default='red']
--cols_to_use_heatmap: # Columns in the heatmap Data file to use and the order from the center up
--ID_heatmap_field: # Column name for IDs found in the tips of the tree in the heatmap Data file
--heatmap_variable: # Use only variable columns in the heatmap
--heatmap_count_by_sep: # Count the sep in each cell to generate the values for the heatmap
--heatmap_HC_dist: # The heatmap Hierarchical Clustering dist method
--heatmap_HC_agg: # The heatmap Hierarchical Clustering agglomeration method
BUSCO
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A class that defines a module for running BUSCO.
BUSCO searches for predefined sequences in an assembly. See the BUSCO website.
This module creates scripts for running BUSCO on a fasta file against a BUSCO lineage database.
The lineage can be specified in two ways:
Specify the path to the lineage file with the
--lineageredirected argument.Specify the URL of the database (e.g. http://busco.ezlab.org/v2/datasets/eukaryota_odb9.tar.gz). The file will be downloaded and unzipped.
Requires
fasta files in one of the following slots for sample-wise BUSCO:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.prot"]
or fasta files in one of the following slots for project-wise BUSCO:
sample_data["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["fasta.prot"]
Output:
Stores output directory in:
self.sample_data[<sample>][“BUSCO”] (
scope = sample)self.sample_data[“project_data”][“BUSCO”] (
scope = project)
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
|
Use sample of project scope fasta file. |
get_lineage |
Path to one of the lineages to download from https://busco.ezlab.org/frame_wget.html. Will be downloaded, unzipped and used if no –lineage is passed. |
Lines for parameter file
Run BUSCO on project-scope fasta file, using a pre-downloaded BUSCO database:
BUSCO1:
module: BUSCO
base: Trinity_assembl
script_path: {Vars.paths.BUSCO}
scope: project
redirects:
--mode: transcriptome
--lineage: {Vars.databases.BUSCO}
--cpu: 65
--force:
--restart:
Run BUSCO on project-scope fasta file, including downloading the BUSCO database:
BUSCO1:
module: BUSCO
base: Trinity_assembl
script_path: {Vars.paths.BUSCO}
scope: project
get_lineage: http://busco.ezlab.org/v2/datasets/eukaryota_odb9.tar.gz
redirects:
--mode: transcriptome
--cpu: 65
--force:
--restart:
References
Miscellaneous Modules
Modules included in this section
manage_types *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for managing file type without script creation.
Supports adding, deleting, copying and moving file types.
Requires
Output
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
operation |
add|del|mv|cp |
The operation to perform on the file type dictionary |
scope |
project|sample |
The scope on which to perform the operation. For ‘mv’ and ‘cp’ this is the source scope |
type |
The type on which to perform the operation. For ‘mv’ and ‘cp’ this is the source type |
|
scope_trg |
project|sample |
The destination scope for ‘mv’ and ‘cp’ operations |
type_trg |
The destination type for ‘mv’ and ‘cp’ operations |
|
path |
For ‘add’ operation, the value to insert in the file type. |
Attention
The operations do NOT operate on the actual files! They only modify internal file types index.
Tip
You can combine several operations in one module instance, by passing lists to the parameters in the table above. All lists should be of the same length, or of length 1 (i.e. plain strings). Plain strings will be extrapolated to all operations. e.g., to delete one file type and add another, both at the project scope, pass [del,add] to the ‘operation’ parameter, and ‘project’ to the ‘scope’ parameter. The ‘path’ can also be a plain string. It will be extrapolated to ‘del’, as well, but will be ignored by it. See example lines below.
Lines for parameter file
manage_types1:
module: manage_types
base: STAR_bld_ind
script_path:
scope: project
operation: mv
type: trinity.contigs
type_trg: trinity.contigs
scope_trg: sample
manage_types1:
module: manage_types
base: trinity1
script_path:
scope: - project
- sample
- sample
- project
operation: - mv
- del
- cp
- add
type: - fasta.nucl
- fasta.nucl
- fastq.F
- bam
type_trg: [transcripts.nucl, None ,fastq.main, None]
scope_trg: sample
path: /path/to/mapping.bam
merge_table
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for merging sample tables into a single project-wide table, or into group tables by category.
The table can be with or without a header line.
Can be used for merging fasta and fastq files as well.
Important
When merging by category, the sample names will be set to the category level names for all subsequent steps.
Tip
You can merge several types at once by passing them as a list to type. If the type files have different numbers of header lines, pass a list of header line numbers with header. The header list must be of length 1 or identical to the length of type.
The extension of the resulting file will be the same as that of the files being merged, if they are all the same. If not, will not add an extension. To change the default behaviour, set an ext parameter with the extension to use, e.g. fna. If several types are being merged, if ext is a string, the string will be used for all types. For a different ext for each file type, use a list of strings, in the same order as the type parameter.
Attention
If you split sample-scope fasta files with fasta_splitter or split_fasta modules, the new subsamples are stored with a source category, containing the sample name from which the subsample was produced. When merging back into the sample scope, use scope: group and category: source.
Requires
A table file in any slot:
sample_data[<sample>][<file.type>]
Output
Puts output files in the following slot:
sample_data["project_data"][<file.type>]
Or, for merging by category, in the following slot:
sample_data[category_level][<file.type>]
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
type |
A file type that exists in all samples. Can also be a list of types, each one of which will be merged independently |
|
script_path |
Leave blank |
|
scope |
project|group |
Merge all samples into one project table, or merge sample tables by category. |
category |
If |
|
header |
0 |
The number of header lines each table has. The header will be used for the complete table and all other headers will be removed. If there is no header line, set to 0 or leave out completely. If set but not specified, will default to 1!. |
ext |
The extension to use for the merged file. If |
|
add_filename |
If set, the source filename will be appended to each line in the resulting table. |
Lines for parameter file
Merge sample-scope tables into single project-scope table:
merge_blast_tables:
module: merge_table
base: merge1
script_path:
scope: project
type: blast.prot
header: 0
Merge sample-scope tables into group-scope table, by category country:
merge_blast_tables:
module: merge_table
base: merge1
script_path:
scope: group
category: country
type: blast.prot
header: 0
split_fasta
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for splitting fasta files into parts.
Convenient for parallelizing processes on the cluster. You can take a project wide fasta file (such as a transcriptome), split it into sub-fasta files, and run various processes on the sub-files.
The parts can then be combined with merge_table module, which can concatenate any type of file.
Important
When splitting sample-scope fasta files, the subsamples are stored with a source category set to the
original sample name. You can use this for merging results at the sample scope downstream.
See documentation for merge_table.
Requires
A fasta file in one of the following slots (scope = “project”):
sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.prot"]
A fasta file in one of the following slots (scope = “sample”):
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.prot"]
Output
Puts output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.prot"]
For sample scope, the original sample list will be overridden with the new sample list.
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
type |
nucl|prot |
The type of fasta file to split |
subsample_num |
Number of fragments |
Lines for parameter file
split_fasta1:
module: split_fasta
base: Trinity1
script_path:
type: nucl
subsample_num: 4
fasta_splitter
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A module for splitting fasta files into parts, using fasta-splitter.pl.
Convenient for parallelizing processes on the cluster. You can take a project wide fasta file (such as a transcriptome), split it into sub-fasta files, and run various processes on the sub-files.
The parts can then be combined with merge_table module, which can concatenate any type of file.
Attention
The module ships with fasta-splitter.pl version 0.2.6, 2017-08-01.
Leave script_path empty to use the perl script provided. Perl must be in the path!
To use a different version, supply it via script_path.
Usage:
Usage: fasta-splitter [options] <file>...
Options:
--n-parts <N> - Divide into <N> parts
--part-size <N> - Divide into parts of size <N>
--measure (all|seq|count) - Specify whether all data, sequence length, or
number of sequences is used for determining part
sizes ('all' by default).
--line-length - Set output sequence line length, 0 for single line
(default: 60).
--eol (dos|mac|unix) - Choose end-of-line character ('unix' by default).
--part-num-prefix T - Put T before part number in file names (def.: .part-)
--out-dir - Specify output directory.
--nopad - Don't pad part numbers with 0.
--version - Show version.
--help - Show help.
You can’t use the --part-size method, since it will end up in an unknown number of files, which is not defined in Neat-Seq Flow.
Please do not use the --nopad parameter. There is no reason to…
Important
When splitting sample-scope fasta files, the subsamples are stored with a source category set to the
original sample name. You can use this for merging results at the sample scope downstream.
See documentation for merge_table.
Requires
A fasta file in one of the following slots (scope = “project”):
sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data["project_data"]["fasta.prot"]
A fasta file in one of the following slots (scope = “sample”):
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.prot"]
Output
Puts output files in the following slots:
sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.nucl"]sample_data[<sample>]["fasta.prot"]
For sample scope, the original sample list will be overridden with the new sample list.
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
nucl|prot |
The type of fasta file to split |
|
Number of fragments |
Lines for parameter file
split_fasta1:
module: fasta_splitter
base: Trinity1
script_path:
type: nucl
redirects:
--n-parts: 4
--measure: seq
References
ProjectToSample *
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
A utility module for moving project data to a sample, and back again. Is useful when a module which works on sample data has to be executed on data in the project scope.
For instance, in the STAR 2 pass pipeline, the first stage involves aligning all reads to the reference in order to find splice junctions.
The reads can be merged into a project scope fastq.F and fastq.R slots, but all aligners take there reads from the sample scope!
This module overrides the sample list with a single sample containing the project slots (or a subset of the slots). Then, the mapping modules will take the project-wide reads from the sample representing the project.
Recovering the old sample list is done by setting the direction parameter to smp2proj.
See the STAR2pass workflow for the working example.
Usually, the module should be called twice, once in the proj2smp direction and the in the smp2proj direction.
Although it is possible to use the smp2proj to move data from sample sample_name to the project, it is better to do this operation with the manage_types module.
Requires
Output
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
direction |
proj2smp|smp2proj |
Move project info to sample or vice versa |
type |
The types to operate on |
|
operation |
cp|mv |
Whether to move the slots or just copy them. |
sample_name |
The name of the new sample to create or the sample to copy from. Defaults to project title |
Attention
This moduel does NOT operate on the actual files! It only modifies internal file types index.
Lines for parameter file
Moving from project to sample:
ProjectToSample:
module: ProjectToSample
base: merge_table
script_path:
direction: proj2smp
# sample_name: fromproj
operation: mv # mv or cp
type: [fastq.F,fastq.R]
Copying from sample to project:
SampleToProject:
module: ProjectToSample
base: STAR_map_proj
script_path:
direction: smp2proj
operation: mv # mv or cp
type: SJ.out.tab
Copying and moving from sample to project: (Just for the example. Isn’t necessarily practical)
SampleToProject:
module: ProjectToSample
base: STAR_map_proj
script_path:
direction: smp2proj
operation: [cp, mv, mv] # mv or cp
type: [SJ.out.tab, fastq.F, fastq.R]
Generic Modules
The generic modules, called Generic and Fillout_Generic, do not contain a definition of input and output file types, therefore the user has to specify the input and output file types in the parameter file.
Genericis simpler to use for defining most Linux programs, and has extra file type management capacities.Fillout_Genericcan incorporate more than one command per step, as well as cater to irregular program calls, such as calls including complex pipes; however, using it is slightly more complicated.
Modules included in this section
Generic
- Authors
Liron Levin
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Short Description
A generic module that enables the user to design new modules that can handle most cases.
Requires
In this module the users define the required file types in the inputs section
Output
In this module the users define the output file types in the outputs section
The scope of the output file types is determinant by the module scope
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
scope |
sample/project |
The scope of this module could be sample/project, the default is by sample |
shell |
csh/bash |
Type of shell [csh OR bash]. bash is the default, only bash can be used in conda environment |
inputs_last |
The inputs arguments will be at the end of the command |
Comments
The order of the input/output arguments in the final command will be according to the order of their appearance in the parameter file. The redirect arguments are always first.
Example of usage and implementation of the generic module:
Attention
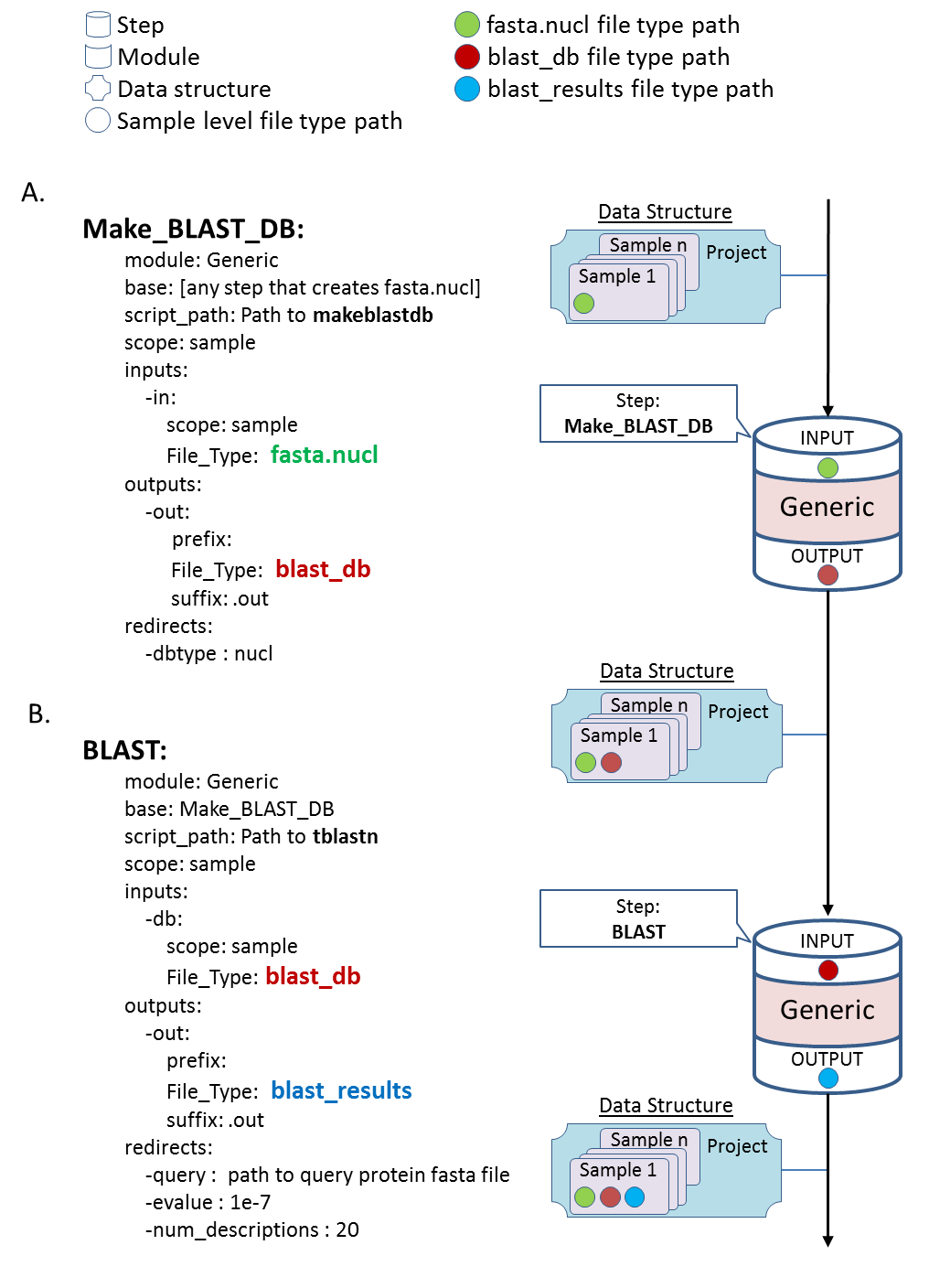
A generic module is used to generate a BLAST database for each sample and a subsequent generic step queries each database with sequences from an external FASTA file. This example is a typical use of BLAST in many biological scenarios such as searching for virulence/resistance genes (whose sequences are in the external FASTA file) in bacterial genomes
A. Calling a generic module to generate a BLAST database (using makeblastdb) from each sample. This step can be used after (base:) any step that creates a nucleotide FASTA file (File_Type: fasta.nucl), e.g. after merge (if the raw files are in nucleotide FASTA format) or after a de novo assembly step. The location of the BLAST database for each sample is saved as a blast_db file type (File_Type: blast_db) for downstream use. B. Calling a generic module which performs a BLAST search (tblastn) of an external query protein fasta file (-query : path to query protein fasta file) against the previously generated BLAST data base per sample. This step can be used after the Make_BLAST_DB step (base: Make_BLAST_DB). The user can pass additional parameters directly to the used program in the redirects section (e.g. –dbtype, –evalue, -num_descriptions etc.).
Lines for parameter file
Step_Name: # Name of this step
module: Generic # Name of module
base: # Name of the step [or list of names] to run after [must be after steps that generates the inputs File_Types]
script_path: # Main command for this module
scope: # The scope of this module could be sample/project, the default is by sample
shell: # Type of shell [csh OR bash]. bash is the default. only bash can be used in conda environment
arg_separator: # The separator between the arguments and values [The default is space].
inputs_last: # The inputs arguments will be at the end of the command. [The default is inputs arguments at the beginning of the command]
command_order: # The order of the command parts as string default 'redirects,inputs,outputs' ignored if inputs_last is set.
use_base_dir: # Use the base step directory as the output for this step, it is possible to specify the base to use.
cd: # Change current working directory to the output location.
no_sample_dir: # In Sample Scope: will NOT create a dedicated folder for each sample and the location of the base folder will be stored
# in a project level 'base_dir' File_Type
remove_subsamples: # Will remove subsamples created by previous steps (split_fasta for example)
subsamples_string: # A string to identify a subsample, all subsample will start with this string. [default: 'subsample']
inputs: # The inputs for this module
STR: # Input argument, e.g. -i, --input [could be also 'empty1', 'empty2'.. for no input argument string]
scope: # The scope of this input argument could be sample/project
# If the module scope is project and the argument scope is sample:
# all the samples inputs File_Types of this argument will be listed as: [input argument] [File_Type(sample#)] e.g. -i sample1.bam -i sample2.bam ...
File_Type: # The input File_Type could be any File_Type available from previous (in this branch) steps
# It is possible to indicate more then one File_Type separated by comma 'fastq.F,fastq.R'
base: # From which previous step to take the input File_Type. The default is the current step.
sep: # If the module scope is project and the argument scope is sample:
# All the samples inputs File_Types of this argument will be listed delimited by sep. e.g. [sep=,] -i sample1.bam,sample2.bam ...
# If more then one File_Type was specify the inputs File_Types of this argument will be listed delimited by sep.
prefix: # A prefix for this input argument file name
preprefix: # A prefix for this input argument file location
suffix: # A suffix for this input argument file name
use_dirname: # Use only the input Directory and add suffix for constant file name and prefix to add a string before the input Directory
del: # Delete the files in the input File_Type after the step ends [use to save space for large files you don't need downstream]
# Will generate empty file with the same name and a suffix of _DELETED
constant_value: # use a constant value instead of "File_Type".
# it is the same as the "redirects".
# use when the order of inputs are important!!
# use '{{sample_name}}' to be replace with the sample name (or project name in project scope)
# using the constant_value option will override all other input arguments!!!!!!
outputs: # The outputs for this module
STR: # Output argument, e.g. -o, --out , the scope of the output arguments is determinant by the module scope
# could be also 'empty1', 'empty2'.. for no output argument string OR 'No_run1', 'No_run2'.. for only entering the file information to output File_Type
File_Type: # The output File_Type could be any File_Type name for the current branch downstream work
# If the File_Type exists its content will be override for the current branch downstream work
prefix: # A prefix for this output argument file name
suffix: # A suffix for this output argument file name
# between prefix and suffix will be the sample name [in sample scope] or the project title [in project scope]
constant_file_name: # Use constant file name for this output argument [ignore prefix and suffix]
# If empty [''] will enter the output directory location
use_base_name: # use only the base name of the output file [ignored if constant_file_name is used]
copy_File_Types: # Transferring information between File_Types
STR: # Unique name for the transfer
source:
File_Type: # Copy the content of source File_Type to the target File_Type [copy from here]
scope: # Copy the source File_Type From this scope [if not specified the default is sample]
base: # The source step to copy the File_Type from (from previous steps). The default it the current step.
constant_value: # Use to transfer information outside of the 'File_Type' system to a File Type, will always be considered as project scope
# Using the constant_value option will override all other source arguments!!!!!!
target:
File_Type: # Copy the content of source File_Type to the target File_Type [copy to here]
scope: # Copy to the target File_Type in this scope [if not specified the default is sample]
qsub_params: # Parameters for qsub [number of cpus or memory to reserve etc ]
STR:
redirects: # Parameters to pass directly to the command
STR:
Fillout_Generic
- Authors
Menachem Sklarz
- Affiliation
Bioinformatics core facility
- Organization
National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben Gurion University.
Description
This module enables executing any type of bash command, including pipes and multiple steps.
File and directory names are embedded in the script by describing the file or directory in a {{}} block, as follows:
1. File names:
Include 4 colon-separated fields: (a) scope, (b) slot, (c) separator and (d) base.
For example: {{sample:fastq.F:,:merge1}} is replaced with sample fastq.F files from merge1 instance, seperated by commas (only for project scope scripts, of course).
Leave fields empty if you do not want to pass a value, e.g. {{sample:fastq.F}} is replaced with the sample fastq.F file.
2. Sample and project names:
You can include the sample or project names in the script by leaving out the file type field. e.g. {{sample}} will be replaced by the sample name.
To get a list of sample names, set the separator field to the separator of your choice, e.g. {{sample::,}} will be replaced with a comma-separated list of sample names.
3. Directories
You can include two directories in your command:
Dir descriptor |
Result |
|---|---|
|
Returns the base directory for the step. |
|
Returns the active directory of the script. For project-scope scripts, this is identical to |
Tip
You can obtain the base_dir or dir values for a base step, by including the name of the base in the 4th colon separated position, just as you’d do for the file slots. e.g. {{base_dir:::merge1}} will return the base_dir for step merge1 and {{dir:::merge1}} will return the dir for the current sample for step merge1.
3. Outputs
Will be replaced with the filename specified in the named output. e.g. {{o:fasta.nucl}} will be replced according to the specifications in the output block named fasta.nucl.
Each output block must contain 2 fields: scope and string. The string contains a string describing the file to be stored in the equivalent slot. In the example above, there must be a block called fasta.nucl in the output block which can be defined as shown in the example in section Lines for parameter file below.
3. Examples
The following examples cover most of the options:
File descriptor |
Result |
|---|---|
|
The |
|
The |
|
A comma-separated list of the |
|
The project name |
|
The sample name |
|
A comma-separated list of sample names |
|
A comma-separated list of the |
Tip
For a colon separate list of sample names or files, use the word ‘colon’ in the separator slot.
Note
The separator field is ignored for project-scope slots.
Attention
If a sample-scope slot is used, in the inputs or the outputs, the scripts will be sample-scope scripts. Otherwise, one project-scope script will be produced. To override this behaviour, set scope to project.
However, you cannot set scope to project if there are sample-scope fields defined.
Requires:
Customizable
Output:
Customizable
Parameters that can be set
Parameter |
Values |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
output |
A block including ‘scope’ and ‘string’ definining the script outputs |
|
scope |
|
The scope of the resulting scripts. You cannot set scope to project if there are sample-scope fields defined. |
Lines for parameter file
Demonstration of embedding various files and titles in a script file:
pipe_gen_3:
module: Fillout_Generic
base: pipe_gen_2
script_path: |
project: {{project}}
fasta.nucl in project: {{project:fasta.nucl}}
fasta.nucl in project from base merge1: {{project:fasta.nucl::merge1}}
sample names: {{sample::,}}
fastq.F in sample: {{sample:fastq.F}}
fastq.F in sample from base merge1: {{sample:fastq.F::merge1}}
output:fasta.nucl: {{o:fasta.nucl}}
output:
fasta.nucl:
scope: project
string: "{{base_dir}}{{project}}_new_pipegen3.fasta"
Comments